-
Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors designed to reduce electromagnetic interference in ignition systems
Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors Designed to Reduce Electromagnetic Interference in Ignition SystemsEvery spark in an automotive ignition system is a miniature lightning bolt radiating elec...
-
Ignition Resistor for Fuel Injection Systems: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & High Resistance Issues in Gasoline Engines
1. How Ignition Resistors Work in Fuel Injection SystemsIgnition resistors in fuel injection systems limit the primary current flowing to the ignition coil, preventing overheating and ensuring the coi...
-
What is an Ignition Resistor?
What is an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & SolutionsIntroductionAn ignition resistor (also called a ballast resistor) is a crucial but often overlooked component in vehicle ignition sy...
-
what is the purpose of an ignition resistor

What Is the Purpose of an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & FixesAn ignition resistor is a crucial but often overlooked component in many combustion engines. Whether you're dealing w...
-
Hybrid Vehicle Ignition Resistor Function: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & Fuel Efficiency Issues in Modern Hybrids
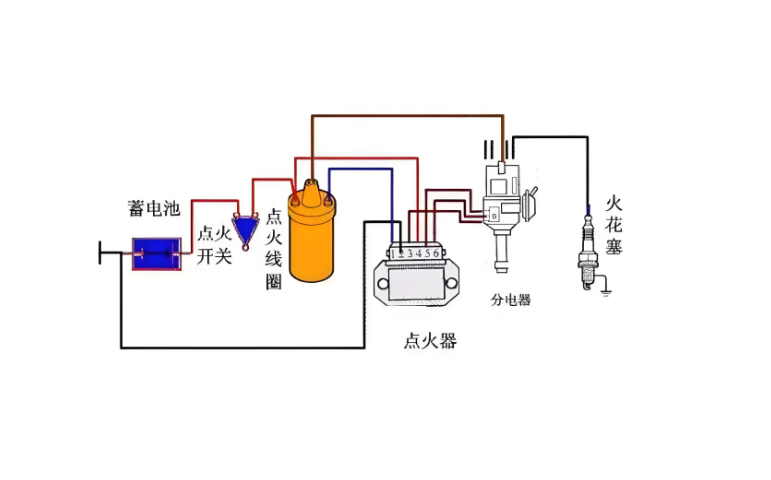
1. What Does the Hybrid Ignition Resistor DoThe hybrid ignition resistor is a specialized component designed to limit primary current to the ignition coil, preventing overheating while ensuring the co...
-
How to Choose Alloy Resistors for High - Reliability Electronic Systems

IntroductionIn high-reliability electronic systems, the selection of components is critical to ensuring consistent performance and longevity. Alloy resistors, with their superior characteristics, are ...
-
High-Precision Alloy Resistors for Battery Management Systems

<!-- Introduction -->Introduction: The Critical Role of Alloy Resistors in Battery ManagementAlloy resistors are indispensable components in modern battery management systems (BMS), ensuring accurate ...
-
180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage Distance Power Resistor | High Voltage Resistance, Non-Inductive Design for Industrial Power Supplies, Motor Control, and Renewable Energy Systems

1. Key Technical Specifications of the 180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage Distance Power ResistorTo understand why this resistor stands out, let’s break down its core parameters—critical for e...
-
Optimizing Electric Traction Systems with High-Performance Carbon Disc Resistors: Applications, Benefits & Selection Tips
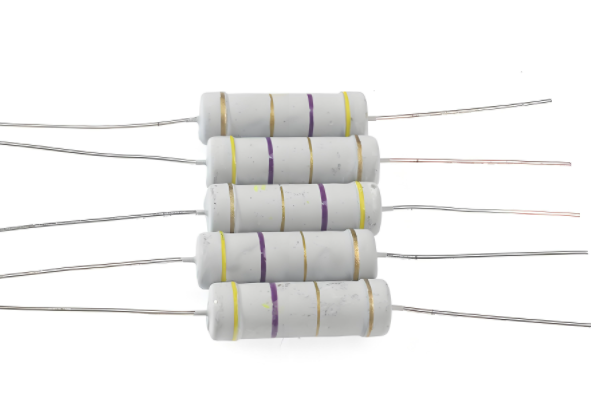
Optimizing Electric Traction Systems with High-Performance Carbon Disc Resistors: Applications, Benefits & Selection Tips<nav></nav>IntroductionElectric traction systems are at the heart of modern...
-
Ensuring Charger Safety: The Critical Role of Safety Resistors in Modern Power Systems
![]()
IntroductionIn today's fast-paced world, the safety and reliability of electronic devices are paramount. Chargers, as essential components of modern power systems, play a crucial role in ensuring ...
-
50kV High Voltage Resistors: Technical Specs, Industrial Use Cases & How to Choose the Right One for Power Grids, Test Labs & Renewable Systems
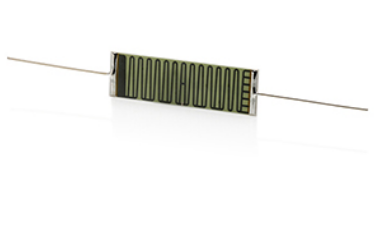
Technical Specifications of 50kV High Voltage Resistors50kV resistors must withstand high electrical stress while maintaining precision. Below are critical parameters to evaluate for reliability in de...
-
100kV High Voltage Resistors: Technical Specs, Harsh Environment Applications & Expert Selection Guide for Power Grids, Particle Accelerators & Industrial Systems

Technical Specifications of 100kV High Voltage ResistorsTo perform reliably in 100kV systems, resistors must meet rigorous performance criteria. Below are critical parameters and their impact on funct...
-
low TCR resistor vs standard chip resistor

Low TCR Resistor vs Standard Chip Resistor: Key Differences & Best ApplicationsIntroductionWhen designing precision circuits, selecting the right resistor type is critical. Two common choices are ...
-
What Does a Safety Resistor Do?

What Does a Safety Resistor Do Key Functions and Protection MechanismsIntroduction: Safety resistors play a critical role in electronic circuit protection, but many engineers misunderstand their full ...
-
What Is a Surge Resistor?

What Is a Surge Resistor Function, Types, and Key ApplicationsIntroduction: Surge resistors are critical components in electronic circuits, protecting sensitive devices from voltage spikes and transie...
-
MELF Resistor Temperature Coefficient: Everything You Need to Know

IntroductionMELF (Metal Electrode Leadless Face) resistors are widely used in various electronic applications due to their superior characteristics. One of the key factors to consider when selecting a...
-
High precision resistor applications

<!-- Introduction -->High Precision Resistor Applications: A 2024 Technical GuideHigh precision resistors are critical components in electronics where stability, accuracy, and low temperature coeffici...
-
What is a High Voltage Cylindrical Resistor?

Introduction: Why the High Voltage Cylindrical Resistor Deserves Your AttentionWhen engineers search for a high voltage cylindrical resistor they are usually facing one of two headaches: extreme volta...
-
Why Your Trimmable Resistor Calibration Fails (And How to Fix It)

<!-- Introduction -->Why Your Trimmable Resistor Calibration Fails (And How to Fix It)Trimmable resistors are essential for precision electronics, but improper calibration can lead to circuit instabil...
-
THT Resistor Tolerance Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide

IntroductionThrough-Hole Technology (THT) resistors are a cornerstone in electronic circuit design, offering stability and reliability. One critical aspect that significantly influences their performa...
-
Hybrid Vehicle Ignition Resistor Function: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & Fuel Efficiency Issues in Modern Hybrids

1. What Does the Hybrid Ignition Resistor DoThe hybrid ignition resistor is a specialized component designed to limit primary current to the ignition coil, preventing overheating while ensuring the co...
-
Ignition Resistor for Fuel Injection Systems: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & High Resistance Issues in Gasoline Engines

1. How Ignition Resistors Work in Fuel Injection SystemsIgnition resistors in fuel injection systems limit the primary current flowing to the ignition coil, preventing overheating and ensuring the coi...
-
Resistor Spark Plug – Spark plugs with built-in resistors
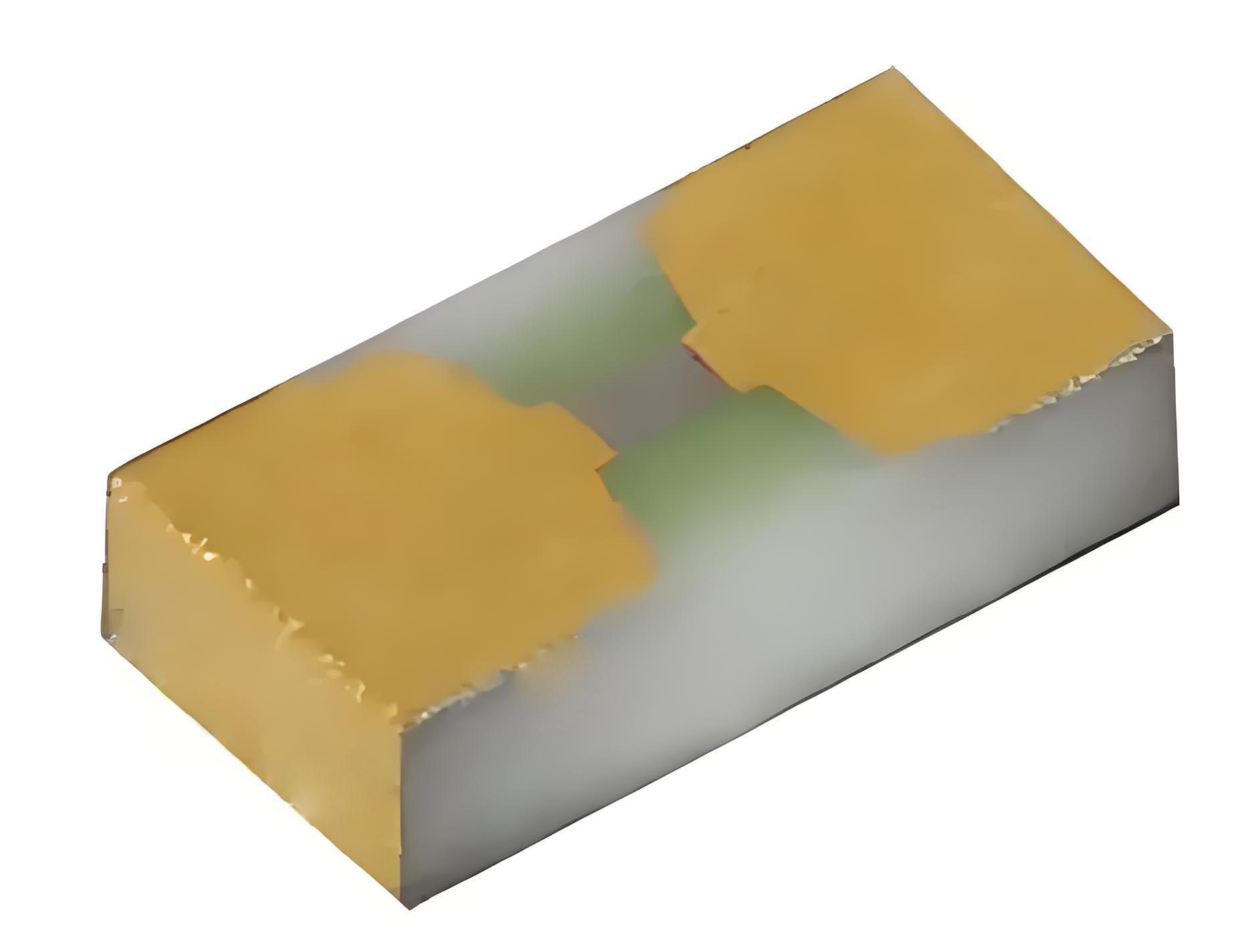
Resistor Spark Plug – Spark Plugs with Built-in ResistorsEvery spark in a modern engine is a miniature lightning bolt that can broadcast harmful radio-frequency interference (RFI). Resistor spark pl...
-
Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors designed to reduce electromagnetic interference in ignition systems

Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors Designed to Reduce Electromagnetic Interference in Ignition SystemsEvery spark in an automotive ignition system is a miniature lightning bolt radiating elec...
-
what is the purpose of an ignition resistor

What Is the Purpose of an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & FixesAn ignition resistor is a crucial but often overlooked component in many combustion engines. Whether you're dealing w...
-
What is an Ignition Resistor?

What is an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & SolutionsIntroductionAn ignition resistor (also called a ballast resistor) is a crucial but often overlooked component in vehicle ignition sy...