Ignition Resistor for Fuel Injection Systems: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & High Resistance Issues in Gasoline Engines
1. How Ignition Resistors Work in Fuel Injection Systems
Ignition resistors in fuel injection systems limit the primary current flowing to the ignition coil, preventing overheating and ensuring the coil generates a high-voltage spark at the correct time. Key parameters include:
| Parameter | Specification | Impact on Fuel Injection |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Value | 0.5–5Ω (varies by vehicle) | Too low: Overheats coil; Too high: Weak spark. |
| Voltage Drop | 0.5–2V (at full load) | Exceeds 2V: Indicates resistor degradation. |
| Temperature Rating | -40°C to +125°C | Exceeding 125°C: Accelerates resistor failure. |
Example: A 2018 Toyota Camry with a 2.5L 4-cylinder engine uses a 1.5Ω ignition resistor. At 3,000 RPM, the primary current should measure 4.5A (V = I×R → 6.75V = 4.5A×1.5Ω). A reading of 6V (4A) or 8V (5.3A) signals a problem.
2. Common Symptoms of a Faulty Ignition Resistor
Faulty ignition resistors manifest in distinct ways. Below are the most frequent issues, paired with real-world data from repair logs:
| Symptom | Frequency (Repair Logs) | Root Cause |
|---|---|---|
| No Spark (Engine Won’t Start) | 42% | Open circuit (resistor burned out) or loose connections. |
| Misfire (Rough Idling, Stalling) | 31% | Intermittent high resistance (e.g., corroded terminals). |
| Hard Starting (Prolonged Cranking) | 18% | High resistance reducing spark energy. |
| Check Engine Light (CEL) Code P0300–P0308 | 9% | Misfire detected by ECU due to weak spark. |
3. Step-by-Step Diagnosis: Tools & Data
Diagnosing ignition resistor issues requires systematic testing. Here’s a proven workflow with data benchmarks:
3.1 Step 1: Visual Inspection
Check for physical damage (cracks, burns) or corrosion on the resistor and its terminals. Use a multimeter to measure resistance across the terminals:
Normal: Matches OEM specs (e.g., 1.5Ω ±5%).
Faulty: Open circuit (OL) or resistance outside spec (e.g., 0.2Ω or 10Ω).
3.2 Step 2: Voltage Drop Test
With the engine running at 2,000 RPM, measure voltage across the resistor:
Normal: ≤2V.
Faulty: >2V (indicates excessive resistance).
3.3 Step 3: Spark Test
Remove the spark plug, reconnect it to the wire, and ground it to the engine. Crank the engine and check for a strong, blue spark:
Normal: Spark jumps 5–8mm.
Faulty: Weak orange spark or no spark.
| Test | Tool | Pass/Fail Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Digital Multimeter (DMM) | Within OEM ±5% range. |
| Voltage Drop | DMM (DC Voltage) | ≤2V at 2,000 RPM. |
| Spark Strength | Spark Tester | Blue spark, 5–8mm gap. |
4. Fixing No Spark, Misfire & High Resistance Issues
Once diagnosed, address the root cause with these solutions:
4.1 Issue 1: No Spark (Open Circuit)
Cause: Resistor burned out, loose terminals, or broken wires. Solution: - Replace the ignition resistor (use OEM part for compatibility). - Clean corroded terminals with electrical contact cleaner. - Re-solder loose connections (for through-hole resistors).
4.2 Issue 2: Misfire (Intermittent High Resistance)
Cause: Thermal expansion/contraction causing loose connections, or carbon buildup. Solution: - Apply dielectric grease to terminals to prevent corrosion. - Use a wire brush to clean carbon deposits from the resistor surface. - Upgrade to a high-temperature resistor (e.g., 150°C rating) for engines prone to overheating.
4.3 Issue 3: High Resistance (Weak Spark)
Cause: Resistor degradation, voltage regulator malfunction, or incorrect part. Solution: - Replace the resistor with one matching OEM resistance (e.g., 1.5Ω for Toyota Camry). - Test the voltage regulator to ensure stable input voltage (12V ±0.5V). - For aftermarket resistors, verify cross-referencing with the vehicle’s VIN.
| Issue | Solution | Tool/Part Needed |
|---|---|---|
| No Spark | Replace resistor; clean terminals | OEM resistor, electrical cleaner |
| Misfire | Clean contacts; upgrade resistor | Dielectric grease, high-temp resistor |
| High Resistance | Replace resistor; test voltage regulator | DMM, OEM resistor |
5. Preventing Future Failures
Extend the life of your ignition resistor with these proactive steps:
| Tip | Frequency | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect terminals for corrosion monthly | Monthly | Prevents intermittent high resistance. |
| Clean resistor surface with compressed air quarterly | Quarterly | Removes debris that causes overheating. |
| Test resistance/voltage drop annually | Annually | Catches degradation before failure. |
| Use dielectric grease on connections | During installation | Seals out moisture and corrosion. |
Understanding ignition resistors for fuel injection systems and their role in preventing no spark, misfire, and high resistance issues is key to maintaining engine performance. By following this guide—using data-driven diagnostics and targeted solutions—you can quickly resolve problems and extend the life of your vehicle’s ignition system. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, this resource equips you to tackle ignition resistor challenges with confidence.
Email us
-
 Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
-
 Jumper Resistor
Jumper Resistor
-
 Ignition Resistor
Ignition Resistor
-
 High Frequency Resistor
High Frequency Resistor
-
 Milliohm Resistor
Milliohm Resistor
-
 Non-Inductive Resistor
Non-Inductive Resistor
-
 Surge Resistor
Surge Resistor
-
 Safety Resistor
Safety Resistor
-
 Aluminum Nitride Resistance
Aluminum Nitride Resistance
-
 High Value Resistors
High Value Resistors
-
 Alloy Resistor
Alloy Resistor
-
 KB RESISTOR
KB RESISTOR
-
 GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
-
 RE power aluminum case wound resistor
RE power aluminum case wound resistor
-
 RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RXHGI high power wane ripple coated wire - wound resistors
RXHGI high power wane ripple coated wire - wound resistors
-
 RX20 high power vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
RX20 high power vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
-
 RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
-
 RXGI high power coated wire - wound resistors
RXGI high power coated wire - wound resistors
-
 RXGM high power coated wire - wound resistors
RXGM high power coated wire - wound resistors
-
 RGFL Power type air cooled module resistor
RGFL Power type air cooled module resistor
-
 RXLB - M Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLB - M Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - A Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLG - A Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - B Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLG - B Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
Ignition Resistor for Fuel Injection Systems: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & High Resistance Issues in Gasoline Engines

1. How Ignition Resistors Work in Fuel Injection SystemsIgnition resistors in fuel injection systems limit the primary current flowing to the ignition coil, preventing overheating and ensuring the coi...
-
Hybrid Vehicle Ignition Resistor Function: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & Fuel Efficiency Issues in Modern Hybrids
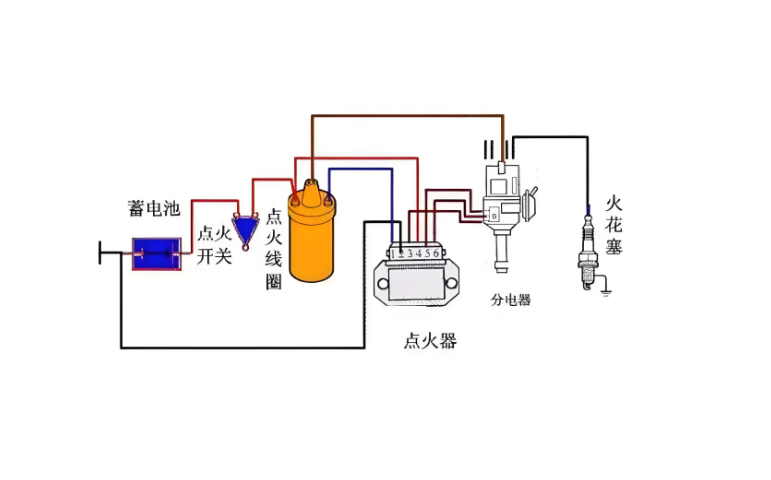
1. What Does the Hybrid Ignition Resistor DoThe hybrid ignition resistor is a specialized component designed to limit primary current to the ignition coil, preventing overheating while ensuring the co...
-
Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors designed to reduce electromagnetic interference in ignition systems
Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors Designed to Reduce Electromagnetic Interference in Ignition SystemsEvery spark in an automotive ignition system is a miniature lightning bolt radiating elec...
-
Resistor Spark Plug – Spark plugs with built-in resistors
Resistor Spark Plug – Spark Plugs with Built-in ResistorsEvery spark in a modern engine is a miniature lightning bolt that can broadcast harmful radio-frequency interference (RFI). Resistor spark pl...
-
180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage Distance Power Resistor | High Voltage Resistance, Non-Inductive Design for Industrial Power Supplies, Motor Control, and Renewable Energy Systems
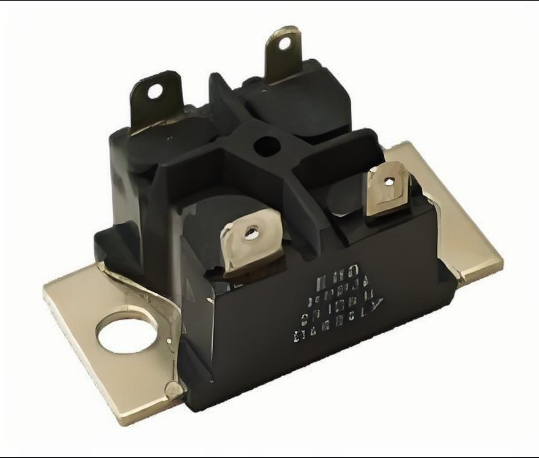

1. Key Technical Specifications of the 180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage Distance Power ResistorTo understand why this resistor stands out, let’s break down its core parameters—critical for e...
-
50kV High Voltage Resistors: Technical Specs, Industrial Use Cases & How to Choose the Right One for Power Grids, Test Labs & Renewable Systems
Technical Specifications of 50kV High Voltage Resistors50kV resistors must withstand high electrical stress while maintaining precision. Below are critical parameters to evaluate for reliability in de...
-
100kV High Voltage Resistors: Technical Specs, Harsh Environment Applications & Expert Selection Guide for Power Grids, Particle Accelerators & Industrial Systems

Technical Specifications of 100kV High Voltage ResistorsTo perform reliably in 100kV systems, resistors must meet rigorous performance criteria. Below are critical parameters and their impact on funct...
-
What is an Ignition Resistor?
What is an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & SolutionsIntroductionAn ignition resistor (also called a ballast resistor) is a crucial but often overlooked component in vehicle ignition sy...
-
what is the purpose of an ignition resistor

What Is the Purpose of an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & FixesAn ignition resistor is a crucial but often overlooked component in many combustion engines. Whether you're dealing w...
-
Optimizing Electric Traction Systems with High-Performance Carbon Disc Resistors: Applications, Benefits & Selection Tips
Optimizing Electric Traction Systems with High-Performance Carbon Disc Resistors: Applications, Benefits & Selection Tips<nav></nav>IntroductionElectric traction systems are at the heart of modern...
-
High Pulse Resistance Surge Resistor: The Ultimate Guide for Reliable Circuit Protection
IntroductionIn the realm of electronics, the reliability and safety of circuits are paramount. Voltage spikes and transient events can wreak havoc on sensitive components, leading to costly repairs an...
-
High-Precision Alloy Resistors for Battery Management Systems
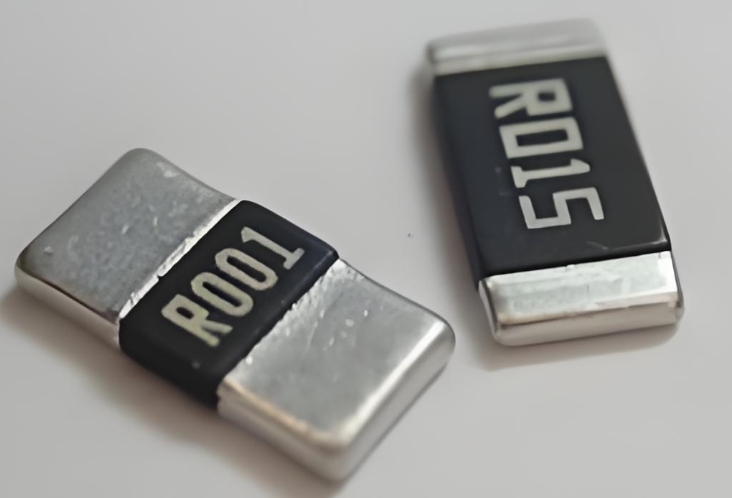

<!-- Introduction -->Introduction: The Critical Role of Alloy Resistors in Battery ManagementAlloy resistors are indispensable components in modern battery management systems (BMS), ensuring accurate ...
-
How to Choose Alloy Resistors for High - Reliability Electronic Systems

IntroductionIn high-reliability electronic systems, the selection of components is critical to ensuring consistent performance and longevity. Alloy resistors, with their superior characteristics, are ...
-
French Blue Baseplate 180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage Resistor | High Voltage Resistance, Non-Inductive Design for Industrial Power Supplies, Motor Control, and Harsh Environments
1. Key Technical Specifications of the French Blue Baseplate 180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage ResistorTo evaluate its suitability for demanding applications, let’s examine its core parameters—...
-
Key Aluminum Nitride Resistance Properties to Specify When Ordering Substrates

IntroductionAluminum Nitride (AlN) substrates are widely used in high-power electronic and optoelectronic applications due to their excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties....
-
The Working Principle of Power Shunt Resistors and Their Low Resistance Characteristics

<!-- 引言部分 -->IntroductionIn the field of electronics and electrical engineering, accurately measuring electrical current is crucial for various applications such as power management, battery m...
-
Aluminum Nitride resistance to molten metals in electronic industry applications
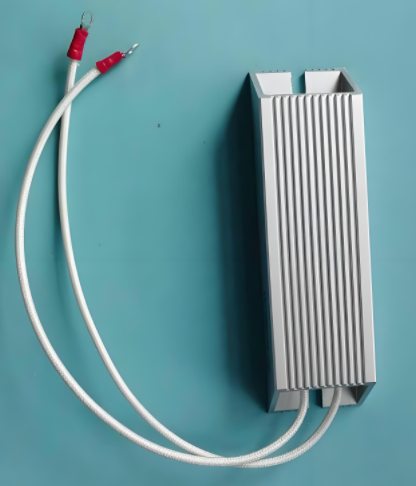

Aluminum Nitride Resistance to Molten Metals in Electronic Industry ApplicationsIn the electronic industry, Aluminum Nitride (AlN) is widely used due to its excellent thermal and electrical insulating...
-
Long-Term Drift Resistance in High Precision Metal Film Resistors

IntroductionHigh precision metal film resistors are renowned for their ability to maintain accurate resistance values over extended periods. The characteristic of long - term drift resistance is a key...
-
Why Aluminum Nitride's Resistance Properties Make It Ideal for RF Applications

IntroductionAluminum Nitride (AlN) has emerged as a critical material in radio frequency (RF) applications due to its exceptional electrical and thermal properties. Its high resistance to electrical b...
-
Low Resistance Shunt Resistors: High-Precision Current Monitoring for Industrial Applications
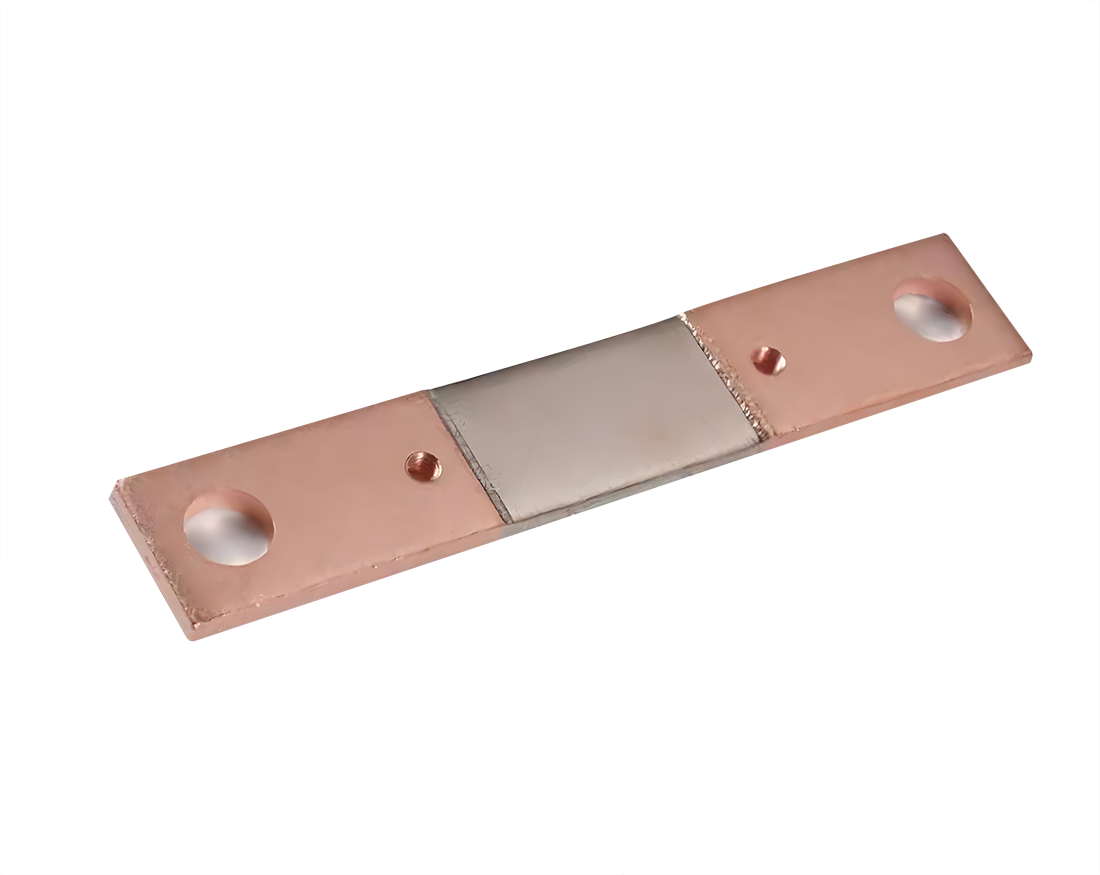

Title: Low Resistance Shunt Resistors: High-Precision Current Monitoring for Industrial ApplicationsIntroductionLow resistance shunt resistors are fundamental components for high-precision current mon...
-
Hybrid Vehicle Ignition Resistor Function: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & Fuel Efficiency Issues in Modern Hybrids

1. What Does the Hybrid Ignition Resistor DoThe hybrid ignition resistor is a specialized component designed to limit primary current to the ignition coil, preventing overheating while ensuring the co...
-
Ignition Resistor for Fuel Injection Systems: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & High Resistance Issues in Gasoline Engines

1. How Ignition Resistors Work in Fuel Injection SystemsIgnition resistors in fuel injection systems limit the primary current flowing to the ignition coil, preventing overheating and ensuring the coi...
-
Resistor Spark Plug – Spark plugs with built-in resistors

Resistor Spark Plug – Spark Plugs with Built-in ResistorsEvery spark in a modern engine is a miniature lightning bolt that can broadcast harmful radio-frequency interference (RFI). Resistor spark pl...
-
Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors designed to reduce electromagnetic interference in ignition systems

Ignition Suppression Resistor – Resistors Designed to Reduce Electromagnetic Interference in Ignition SystemsEvery spark in an automotive ignition system is a miniature lightning bolt radiating elec...
-
what is the purpose of an ignition resistor

What Is the Purpose of an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & FixesAn ignition resistor is a crucial but often overlooked component in many combustion engines. Whether you're dealing w...
-
What is an Ignition Resistor?

What is an Ignition Resistor Function, Failure Signs & SolutionsIntroductionAn ignition resistor (also called a ballast resistor) is a crucial but often overlooked component in vehicle ignition sy...
Resistor Supplies - Jepsun Tech Corporation
JEPSUN INDUSTRIAL is committed to always being one of our customers' favorite suppliers.
+86755-29796190 +8615920026751 [email protected]
Huangjiazhongxin building Donghuan Road Longhua District SHENZHEN City, GUANGDONG Prov. CHINA 518000