Introduction
Through-Hole Technology (THT) resistors are a cornerstone in electronic circuit design, offering stability and reliability. One critical aspect that significantly influences their performance is tolerance. This comprehensive guide delves into THT resistor tolerance specifications, shedding light on their importance, common values, and how to select the right tolerance for your specific application. By understanding these specifications, engineers and hobbyists can optimize their circuit designs for precision and reliability.
Tolerance Overview
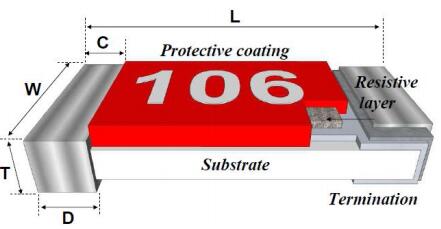
Resistor tolerance refers to the permissible variation in resistance value from its nominal value. For THT resistors, this tolerance is typically expressed as a percentage. Understanding this parameter is crucial because it directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of electronic circuits.
| Tolerance | Description |
|---|---|
| ±1% | High precision, suitable for sensitive circuits |
| ±5% | Standard precision, commonly used in general applications |
| ±10% | Lower precision, suitable for less critical applications |
Common Tolerance Values
THT resistors come with various tolerance values, each tailored to different application requirements. The most common tolerance values are ±1%, ±5%, and ±10%. The choice of tolerance depends on the precision needed for the circuit.
| Tolerance | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|
| ±1% | Precision amplifiers, high-accuracy sensors |
| ±5% | General-purpose circuits, power supplies |
| ±10% | Non-critical applications, basic prototyping |
Importance of Tolerance
The tolerance of a THT resistor affects the overall performance of a circuit. In precision circuits, such as those used in medical equipment or high-accuracy sensors, a tolerance of ±1% is often required to ensure accuracy. Conversely, in less critical applications, a tolerance of ±10% may suffice.
Choosing the wrong tolerance can lead to significant errors in circuit performance. For instance, a resistor with a ±10% tolerance in a precision circuit may cause unacceptable deviations in output.
Selecting the Right Tolerance
Selecting the appropriate tolerance for a THT resistor involves understanding the specific requirements of your circuit. Here are some guidelines to help you make the right choice:
Precision Requirements: Determine the level of precision needed for your application. High-precision circuits require lower tolerance values.
Cost Considerations: Higher precision (lower tolerance) resistors are generally more expensive. Balance precision needs with budget constraints.
Environmental Factors: Consider the operating environment of your circuit. Temperature variations and other factors can affect resistor tolerance.
Problem and Solution
Problem: A common issue faced by engineers is selecting the wrong tolerance for their THT resistors, leading to circuit performance issues.
Solution: To address this, engineers should:
Conduct a thorough analysis of the circuit requirements.
Consult datasheets and technical specifications for recommended tolerance values.
Perform simulations to understand the impact of different tolerance values on circuit performance.
By following these steps, engineers can ensure that the selected THT resistor tolerance aligns with the specific needs of their circuit, thereby enhancing reliability and accuracy.
Conclusion
THT resistor tolerance is a critical specification that engineers must consider when designing electronic circuits. By understanding the common tolerance values, their importance, and how to select the right tolerance, engineers can optimize their designs for precision and reliability. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for making informed decisions regarding THT resistor tolerance, ensuring that your circuits perform as intended.