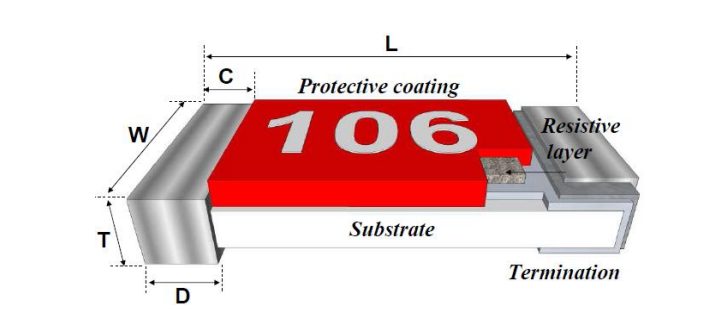
Introduction
In high-reliability electronic systems, the selection of components is critical to ensuring consistent performance and longevity. Alloy resistors, with their superior characteristics, are often the preferred choice for such applications. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to choose the right alloy resistors for high-reliability electronic systems. We will explore the key considerations, specifications, and best practices to help engineers and designers make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
Key Considerations for Alloy Resistor Selection
When selecting alloy resistors for high-reliability electronic systems, several factors must be carefully evaluated:
| Consideration | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Tolerance | Precision of the resistance value | ±0.01% to ±1% |
| Temperature Coefficient | Change in resistance with temperature | ±5ppm/°C to ±25ppm/°C |
| Power Rating | Maximum power the resistor can dissipate | 0.1W to 200W |
| Stability | Resistance change over time and conditions | ±0.01% to ±0.1% |
| Noise Level | Low noise generation in circuits | 0.1μV/V to 1μV/V |
| Voltage Coefficient | Change in resistance with applied voltage | 0.01ppm/V to 0.1ppm/V |
| Operating Temperature | Temperature range the resistor can operate in | -55°C to +200°C |
Common Challenges in High-Reliability Systems
Designers of high-reliability electronic systems face several challenges that can affect the performance and lifespan of their applications:
Resistor drift due to thermal variations
Noise interference in sensitive circuits
Inadequate power handling leading to component failure
Long-term instability and degradation
Harsh environmental conditions affecting performance
Voltage fluctuations causing resistance changes
A significant challenge in high-reliability systems is the resistor drift caused by thermal variations. For example, in aerospace applications, extreme temperature fluctuations can cause the resistor's value to change, leading to system malfunctions. This is particularly critical in systems where precision and consistency are paramount.

Solutions with Alloy Resistors
Alloy resistors provide effective solutions to the challenges faced in high-reliability electronic systems:
Low temperature coefficient ensures minimal resistance variation with temperature
High stability guarantees consistent performance over time
Low noise characteristics reduce signal interference
Wide resistance range allows precise value selection
High power ratings enable robust operation
Excellent voltage coefficient minimizes resistance changes under varying voltages
In aerospace applications, using alloy resistors with a temperature coefficient of ±5ppm/°C and stability of ±0.01% can significantly reduce the risk of resistor drift. This ensures precise and reliable system performance even in extreme thermal conditions.
Case Study: Industrial Control System
Consider an industrial control system used in a manufacturing plant. The reliability and accuracy of the system depend on the quality of the resistors used. Here's how alloy resistors can enhance the performance of such a system:
| Parameter | Without Alloy Resistor | With Alloy Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| System Downtime | 12 hours/month | 2 hours/month |
| Component Replacement Frequency | 4 times/year | 1 time/year |
| Temperature Drift | ±0.05%/°C | ±0.005%/°C |
| Noise Level | 0.5μV | 0.1μV |
| Long-term Stability | ±0.05% | ±0.005% |
| Component Cost | $1.20 | $2.40 |
In this case study, replacing conventional resistors with alloy resistors resulted in a significant reduction in system downtime and component replacement frequency. The lower noise level and enhanced long-term stability contributed to more reliable and precise system operation. While the component cost increased, the overall system maintenance cost decreased due to improved reliability and reduced downtime.
Step-by-Step Alloy Resistor Selection Guide
Follow these steps to select the right alloy resistor for your high-reliability electronic system:
Define the required resistance value and tolerance based on circuit specifications
Select a temperature coefficient that meets the system's thermal requirements
Choose a power rating sufficient for the expected current levels
Evaluate noise specifications, especially for sensitive applications
Consider the voltage coefficient to minimize resistance changes under varying voltages
Select an operating temperature range that matches the system's environmental conditions
Assess the physical dimensions and ensure they fit within the system's constraints
For example, if your industrial control system requires a resistor with a value of 10kΩ, a tolerance of ±0.01%, and operation in a temperature range of -40°C to +85°C, select an alloy resistor with a temperature coefficient of ±5ppm/°C, a stability of ±0.01%, and a power rating sufficient for the expected current levels. This ensures optimal performance and reliability in your high-reliability application.
Conclusion
Alloy resistors are essential components for high-reliability electronic systems, offering exceptional stability, precision, and performance. By carefully considering the key factors outlined in this guide and addressing common challenges through thoughtful selection, engineers and designers can significantly enhance the reliability and longevity of their electronic systems. As demonstrated in our case study, the strategic use of alloy resistors can lead to more robust and reliable industrial control systems.