Understanding the Power Rating of a Resistor: How it Works and Its Applications
What is the Power Rating of a Resistor?
The power rating of a resistor is a specification that indicates the maximum amount of power that the resistor can dissipate without being damaged. It is usually measured in watts (W). Mathematically, power (P) dissipated in a resistor can be calculated using the formula $P = I^{2}R$ (where $I$ is the current flowing through the resistor in amperes and $R$ is the resistance of the resistor in ohms), or $P=frac{V^{2}}{R}$ (where $V$ is the voltage across the resistor in volts).
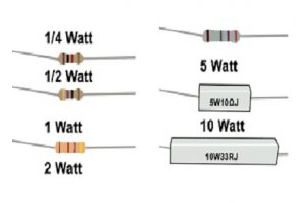
Working Principle Related to Power Rating When current flows through a resistor, electrical energy is converted into heat energy. According to Joule's law of heating, the heat generated ($H$) in a resistor is proportional to the square of the current passing through it, the resistance of the resistor, and the time for which the current flows ($H = I^{2}Rt$). If the power dissipated in the resistor due to the flow of current exceeds its power rating, the temperature of the resistor will rise to a level that can cause damage to the resistor. For example, a resistor with a power rating of 1/4 watt (0.25 W) can handle a certain amount of current and voltage combination. If the power dissipated in the resistor, as calculated by the above formulas, exceeds 0.25 W, the resistor may overheat. Uses of Power Rating in Resistor Selection and Circuit Design 1. Circuit Protection - In a simple LED circuit, if the power supply voltage is known and the resistance value required to limit the current through the LED is calculated, the power rating of the resistor must also be considered. For example, if an LED has a forward voltage of 2 V and is powered by a 5 V supply, and the desired current through the LED is 20 mA (0.02 A), the resistance value can be calculated using Ohm's law ($R=frac{V - V_{LED}}{I}$ where $V$ is the supply voltage and $V_{LED}$ is the LED's forward voltage). Here, $R=frac{5 - 2}{0.02}= 150Omega$. The power dissipated in the resistor is $P = I^{2}R=(0.02)^{2} imes150 = 0.06W$. So, a resistor with a power rating of at least 0.06 W (but it's usually a good idea to choose a slightly higher rating, like 1/8 W or 0.125 W) should be used to ensure the resistor doesn't overheat and fail.
2. Matching Resistors to the Requirements of the Circuit - In a power amplifier circuit, the output stage may have resistors that need to handle significant power. For example, in an audio power amplifier that can deliver 50 W of power to a speaker, the resistors used in the output impedance - matching network may need to have power ratings in the range of several watts. These resistors help to match the output impedance of the amplifier to the impedance of the speaker, ensuring efficient power transfer and minimizing signal distortion. By selecting resistors with appropriate power ratings, the circuit can operate smoothly and reliably, and the resistors will not be damaged due to excessive power dissipation.
Email us
-
 Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
-
 Jumper Resistor
Jumper Resistor
-
 Ignition Resistor
Ignition Resistor
-
 High Frequency Resistor
High Frequency Resistor
-
 Milliohm Resistor
Milliohm Resistor
-
 Non-Inductive Resistor
Non-Inductive Resistor
-
 Surge Resistor
Surge Resistor
-
 Safety Resistor
Safety Resistor
-
 Alloy Resistor
Alloy Resistor
-
 KB RESISTOR
KB RESISTOR
-
 GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
-
 RFX21-T low-power full-short-circuit resistors
RFX21-T low-power full-short-circuit resistors
-
 RXF21-TE power-type full-short-circuit temperature fuse resistors
RXF21-TE power-type full-short-circuit temperature fuse resistors
-
 RE power aluminum case wound resistor
RE power aluminum case wound resistor
-
 RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RX27 power ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
RX27 power ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RXL power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXL power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RXHGI high power wane ripple coated wire - wound resistors
RXHGI high power wane ripple coated wire - wound resistors
-
 RX20 high power vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
RX20 high power vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
-
 RX24 aluminum encased power wire - wound resistors
RX24 aluminum encased power wire - wound resistors
-
 RXLB power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXLB power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
-
 REWR huge power circular edge wound resistors
REWR huge power circular edge wound resistors
-
 RXGI high power coated wire - wound resistors
RXGI high power coated wire - wound resistors
-
Low TCR Resistor Power Rating: Selection Guide, Applications & How to Avoid Overheating
1. What Is a Low TCR Resistor Power RatingThe power rating of a low TCR resistor specifies the maximum power ($P$) it can safely dissipate without exceeding its temperature limit (typically 125°C–1...
-
Carbon Disc Resistor Current Rating: 1A-5A Charts, Power Supply/Audio Use & Overload Fixes

Carbon disc resistors are widely used in low-to-moderate power circuits, but their current rating—how much current they can safely carry without overheating—is a critical parameter often overlooke...
-
600W Power Resistor: Comprehensive Technical Specifications & Applications Explained

600W Power Resistor: Comprehensive Technical Specifications & Applications Explained<!-- 引言 -->IntroductionPower resistors up to 600W play pivotal roles in various industrial sectors like elec...
-
Power Shunt Resistor Applications: From Industrial Equipment to Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicles

IntroductionPower shunt resistors are essential components in various electrical systems, providing critical functions such as current sensing, voltage division, and power management. Their applicatio...
-
600W Wirewound Power Resistor: High - Current Handling and Thermal Stability for Industrial Applications

600W Wirewound Power Resistor: High - Current Handling and Thermal Stability for Industrial ApplicationsIn high - power industrial systems, the 600W wirewound power resistor is a cornerstone component...
-
High Temperature Power Resistors: Applications, Specifications & Selection Guide for Extreme Environments

Table of ContentsIntroductionKey Applications in Extreme EnvironmentsTechnical Specifications & Performance MetricsSelection Guide for High Temperature ResistorsAddressing Thermal Stability Challe...
-
Exploring the Diverse Applications of High Voltage Resistors in Power Generation: Key Roles and Advantages
Applications of High Voltage Resistors in Power GenerationIntroductionIn the intricate realm of power generation, high voltage resistors play a crucial role. They are essential components that help in...
-
180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage Distance Power Resistor | High Voltage Resistance, Non-Inductive Design for Industrial Power Supplies, Motor Control, and Renewable Energy Systems

1. Key Technical Specifications of the 180W Four Terminal Ultra Long Creepage Distance Power ResistorTo understand why this resistor stands out, let’s break down its core parameters—critical for e...
-
High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, and Power Electronics – Selection Guide & Applications

Title: High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, and Power Electronics – Selection Guide & ApplicationsIntroductionThis High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, ...
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using Power Shunt Resistors in Surface Mount Applications for Efficient Current Sensing and Precision Control in Electronics

Benefits of Power Shunt Resistors1. High Precision Current MeasurementPower shunt resistors are known for their exceptional precision in current measurement. With low resistance values and tight toler...
-
10kV High Voltage Resistors: Specifications, Applications & Top Suppliers for Industrial, Power Transmission & Test Equipment

Technical Specifications of 10kV High Voltage ResistorsTo ensure reliability in high-voltage environments, 10kV resistors must meet strict performance criteria. Below are critical parameters to evalua...
-
100kV High Voltage Resistors: Technical Specs, Harsh Environment Applications & Expert Selection Guide for Power Grids, Particle Accelerators & Industrial Systems

Technical Specifications of 100kV High Voltage ResistorsTo perform reliably in 100kV systems, resistors must meet rigorous performance criteria. Below are critical parameters and their impact on funct...
-
Carbon Disc vs Carbon Composition Resistors: Noise, Power Handling & Which to Choose for Audio/Power Circuits

Carbon disc and carbon composition resistors are both legacy components valued for their low cost and organic material composition, but their differences in noise, power handling, and stability make t...
-
Maximizing Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Carbon Disc Resistor Energy Dissipation and Power Handling

IntroductionIn the realm of electronics, the efficiency and reliability of components are paramount. Among these components, carbon disc resistors play a crucial role in various applications, from sim...
-
Alloy Resistor Advantages: Low TCR, High Power Handling & Stability Explained

<!-- Introduction -->Why Alloy Resistors Outperform Traditional OptionsIn precision electronics, resistor selection directly impacts system reliability. Alloy resistors have emerged as superior soluti...
-
100W TO-247 Resistor: High-Power, Non-Inductive & Pulse-Load Resistant Solutions

The Powerhouse Resistor: 100W TO-247 Solutions for Demanding ApplicationsIn high-power electronics, the 100W TO-247 resistor has become a critical component for engineers dealing with pulse loads, the...
-
Why Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Substrates Are Critical for High-Frequency, High-Power Resistor Performance

<nav></nav>IntroductionAs 5G base stations, satellite transponders, and pulsed radar systems push into millimetre-wave bands, the once-obscure aluminum nitride substrate has become the decisive layer ...
-
High precision resistor applications

<!-- Introduction -->High Precision Resistor Applications: A 2024 Technical GuideHigh precision resistors are critical components in electronics where stability, accuracy, and low temperature coeffici...
Resistor Supplies - Jepsun Tech Corporation
JEPSUN INDUSTRIAL is committed to always being one of our customers' favorite suppliers.
+86755-29796190 +8615920026751 [email protected]
Huangjiazhongxin building Donghuan Road Longhua District SHENZHEN City, GUANGDONG Prov. CHINA 518000