600W Wirewound Power Resistor: High - Current Handling and Thermal Stability for Industrial Applications
In high - power industrial systems, the 600W wirewound power resistor is a cornerstone component that delivers steady current handling, rugged thermal stability, and long - term reliability. This article explains how its design, specifications, and mounting options solve real - world problems on the factory floor while meeting the growing demand for high - current wirewound resistors in industrial control boards.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Modern motor drives, power supplies, and braking units require resistors that survive surges, dissipate heat, and maintain stable resistance over decades of service. The 600W wirewound power resistor, built on a mullite-coated ceramic core with corrugated alloy ribbon, is engineered precisely for these demands .
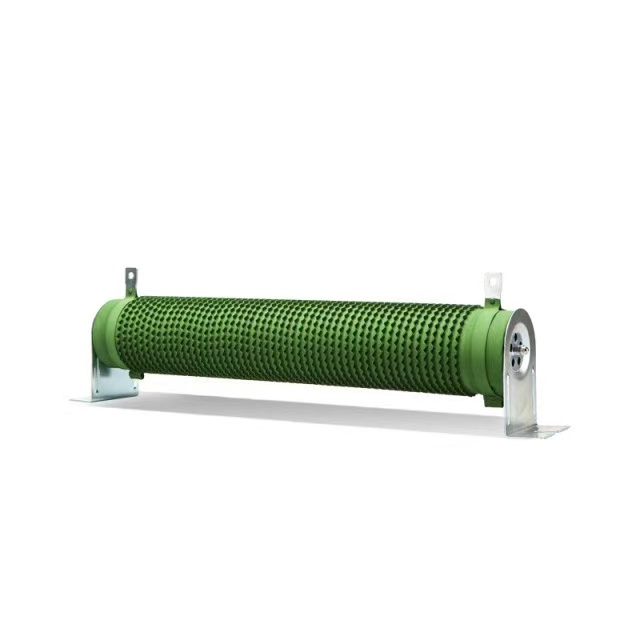

Design & Construction
Element: Corrugated nickel-chromium or copper-nickel alloy ribbon, wound on a tubular ceramic core for rapid cooling and 3× overload for 5 s .
Coating: Non-flammable resin, rated flame-proof at 16× rated power for 5 min .
Terminals: Solder-lug or screw-tab options, 45 N pull-tested for vibration resistance .
Dimensions: L 330 mm × D 50 mm (typical 600 W size) [^13^].
Performance Data
| Parameter | Value | Test Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Power | 600 W | Free air @70 °C |
| Resistance Range | 0.1 Ω – 1 kΩ | E12 series |
| Tolerance | ±5 % (±10 % optional) | 25 °C |
| Temperature Coefficient | ≤ ±440 ppm/°C | -25 °C to +225 °C |
| Dielectric Withstand | AC 2500 V, 1 min | No arc or damage |
| Insulation Resistance | >100 MΩ | 500 V DC |
Industrial Applications
Motor braking: Dynamic braking resistors for 380 VAC VFDs [^15^].
Load banks: Dummy loads for UPS and generator testing.
Capacitor discharge: Safe bleed-off in high-voltage DC links.
Current sensing: Low-ohm shunt elements in welding power sources.
Problem & Solution
Problem: Elevated ambient temperature ( > 70 °C inside cabinets) causes standard resistors to derate excessively, leading to premature failure.
Solution: Utilize the 600 W wirewound resistor’s derating curve—rated to 100 % at 70 °C and linearly down to 0 % at 225 °C—combined with forced-air or base-plate cooling. Mounting the resistor vertically on a 3 mm aluminum plate improves heat dissipation by ~30 %, extending service life beyond 100 000 h .
Best Practices
Keep leads as short as possible to minimize inductive spikes.
Apply thermal compound between resistor base and heat-sink.
Use stainless-steel hardware to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Verify terminal torque (6 N·m) to withstand 200 N tensile test .
Conclusion
With its rugged wirewound construction, wide resistance range, and proven thermal stability, the 600 W power resistor is an optimal choice for demanding industrial applications. Proper mounting and cooling strategies transform it from a simple component into a long-term guarantee of system reliability.