Understanding Thin - Film Resistors: Their Working Mechanisms and Applications
1. What is a Thin - Film Resistor?

A thin - film resistor is a type of resistor that is made by depositing a very thin film of resistive material onto a non - conductive substrate. The thickness of this film is typically in the range of nanometers to micrometers. Common materials used for the resistive film include nichrome (a nickel - chromium alloy), tantalum nitride, and various metal oxides. The substrate is usually made of ceramic or glass, which provides good mechanical stability and electrical insulation.
2. Working Mechanism of Thin - Film Resistors
When a voltage is applied across a thin - film resistor, an electric current flows through the resistive film. According to Ohm's law (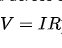 ), the resistance (R) of the thin - film resistor determines the amount of current (I) that will flow for a given voltage (V). The resistance value is mainly determined by the resistivity of the material used in the film, the thickness of the film, and its length and width.
), the resistance (R) of the thin - film resistor determines the amount of current (I) that will flow for a given voltage (V). The resistance value is mainly determined by the resistivity of the material used in the film, the thickness of the film, and its length and width.
The electrons in the current face resistance as they move through the film due to collisions with the atoms of the resistive material. These collisions cause the electrons to lose energy, which is dissipated as heat. The heat dissipation in thin - film resistors is relatively efficient because of the close contact between the thin film and the substrate. The substrate can act as a heat sink, helping to keep the temperature of the resistor within an acceptable range.
For example, if we consider a thin - film resistor with a resistance value of 100 ohms and a voltage of 10 volts applied across it, using Ohm's law, the current flowing through it will be 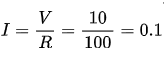 amperes.
amperes.
3. Applications of Thin - Film Resistors
Email us
-
 Moisture Resistant Resistors
Moisture Resistant Resistors
-
 High Value Resistors
High Value Resistors
-
 Lead-Free Resistors
Lead-Free Resistors
-
 Anti-Sulfur Resistors
Anti-Sulfur Resistors
-
 Low TCR Resistors
Low TCR Resistors
-
 Precision Resistors
Precision Resistors
-
 WFL Plastic-Encased Precision Metal Film Strip Chip Shunt
WFL Plastic-Encased Precision Metal Film Strip Chip Shunt
-
 BFL Precision Metal Film Strip Chip Shunts
BFL Precision Metal Film Strip Chip Shunts
-
 RXF21A/B/C (FRT) wire - wound fusing resistors
RXF21A/B/C (FRT) wire - wound fusing resistors
-
 RFX21-T low-power full-short-circuit resistors
RFX21-T low-power full-short-circuit resistors
-
 RFX21-D semi-short-circuit surge-resistant wirewound resistors
RFX21-D semi-short-circuit surge-resistant wirewound resistors
-
 MZ60 metal-film thermistors
MZ60 metal-film thermistors
-
 RF10 painted thin-film fuse resistors
RF10 painted thin-film fuse resistors
-
 RF11 porcelain-cased thin-film fuse resistors
RF11 porcelain-cased thin-film fuse resistors
-
 RWF molded wirewound fuse resistors
RWF molded wirewound fuse resistors
-
 RXG21 (A/B/C/D) lightning surge-resistant wirewound resistors
RXG21 (A/B/C/D) lightning surge-resistant wirewound resistors
-
 RXF21-TE power-type full-short-circuit temperature fuse resistors
RXF21-TE power-type full-short-circuit temperature fuse resistors
-
 RX22 Vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
RX22 Vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
-
 RX23 ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
RX23 ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RX92 anti - interference wire - wound resistors
RX92 anti - interference wire - wound resistors
-
 RX21 coated wire - wound resistors
RX21 coated wire - wound resistors
-
 RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RX27 power ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
RX27 power ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
-
 RXL power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXL power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
-
Thin Film Precision Resistors: Benefits and Applications for High - Accuracy Electronics
Thin Film Precision Resistors: Benefits and Applications for High - Accuracy ElectronicsThin film precision resistors have become indispensable in high - accuracy electronic applications. This article...
-
High Frequency Resistor up to 40 GHz: Thin Film Solutions for RF Applications

High Frequency Resistor up to 40 GHz: Thin Film Solutions for RF Applications<nav></nav>IntroductionIn the realm of high-frequency electronics, the demand for reliable and efficient components has nev...
-
High Voltage Resistors: Working Principle, Applications, Safety Tips & How to Choose the Right One
<!-- Introduction -->IntroductionHigh voltage resistors are critical components in circuits requiring precise voltage control under extreme electrical stress. Understanding their working principle, ap...
-
Thin Film vs. Thick Film: Which High-Frequency Resistor Technology is Best for Your 5G PCB?

Introduction: The Heart of the Matter in 5G DesignThe relentless drive for faster data rates, lower latency, and higher network density in 5G technology pushes every component on a PCB to its performa...
-
Professional High Voltage Thin Film MELF Resistors

High Voltage resistor with the size from 0402 to 2512, resistance up to 100M ohm , offers Max overload to 4000V in 2512, 3000V in 2010.Thick Film special design to achieve high working voltage and sta...
-
Precision Automotive High Voltage Thin Film MELF Resistors

Metal Film Precision High VoltageMELF Resistor (CSRP Series)500V-1000VCSRP±0.1%±0.25%±0.5%±1%0204 0207MELF High Voltage Resistor(CSRH Series)1500V-2500VCSRH±1 ±5%0207 0309ESD Surge ...
-
The Working Principle of Power Shunt Resistors and Their Low Resistance Characteristics

<!-- 引言部分 -->IntroductionIn the field of electronics and electrical engineering, accurately measuring electrical current is crucial for various applications such as power management, battery m...
-
High Performance Metal Film Resistors for Moisture-Prone Applications
Introduction to High Performance Metal Film ResistorsIn electronic circuit design, selecting appropriate resistors is crucial, especially for devices operating in challenging environments. This articl...
-
High Precision Metal Film Resistors: Ultra-Low Tolerance for Demanding Applications

High precision metal film resistors are highly suitable for a variety of specialized fields, prominently including analog signal acquisition and precision instruments and meters.In the realm of analog...
-
Trimmable Thick Film Resistor Characteristics: Detailed Insights into Key Features, Applications, and Selection Criteria for Engineers

Trimmable Thick Film Resistor Characteristics: Detailed Insights into Key Features, Applications, and Selection Criteria for EngineersTrimmable thick film resistors are essential components in various...
-
Trimmable Thick Film Chip Resisto

Trimmable Thick Film Chip Resistor: Unique Advantages and Application ScenariosResistors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, and selecting the right type can significantly impact the pe...
-
Thick Film Chip Resistors, High Voltage

High Voltage Low VCR Thick Film Chip Resistor - HVRC SeriesDerating CurveHigh Voltage Low VCR resistor with the size from 1206 to 2512, resistance up to 500M ohm , offers Max overload to 4000V in 2512...
-
High Voltage (Up to 3 kV) Thick Film Chip Resistors

High Voltage (Up to 3 kV) Thick Film Chip Resistors are crucial electronic components in the modern electronics field. Below is a detailed overview of their key features and attributes:Key Characteris...
-
Advanced Noise Reduction with High Precision Metal Film Resistors

In the realm of modern electronics, noise is an ever-present adversary that can compromise the performance and integrity of circuits. High precision metal film resistors have emerged as a powerful sol...
-
Achieve ±0.01% Tolerance with High Precision Metal Film Resistors
In the field of electronic components, high precision metal film resistors stand out as the key to applications that demand ultimate accuracy. “Achieve ±0.01% Tolerance” indicates that it is poss...
-
Temperature-Stable High Precision Metal Film Resistors for Critical Designs

Temperature-Stable High Precision Metal Film Resistors are indispensable components when it comes to critical designs in various sophisticated electronic systems.These resistors are meticulously engin...
-
Carbon vs. Metal Film vs. Wirewound: Choosing a Resistor for High Pulse Loads

Carbon vs. Metal Film vs. Wirewound: Choosing a Resistor for High Pulse LoadsSelecting the right resistor for high pulse load applications is a critical decision that can make or break your circuit...
-
Long-Term Drift Resistance in High Precision Metal Film Resistors

IntroductionHigh precision metal film resistors are renowned for their ability to maintain accurate resistance values over extended periods. The characteristic of long - term drift resistance is a key...
Resistor Supplies - Jepsun Tech Corporation
JEPSUN INDUSTRIAL is committed to always being one of our customers' favorite suppliers.
+86755-29796190 +8615920026751 [email protected]
Huangjiazhongxin building Donghuan Road Longhua District SHENZHEN City, GUANGDONG Prov. CHINA 518000