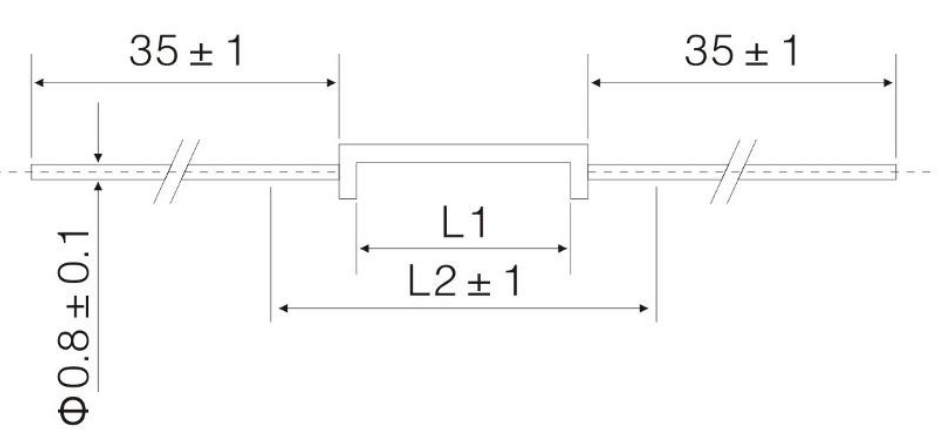
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of telecommunications, the need for efficient and reliable power management and signal processing has never been more critical. One often overlooked yet crucial component in this domain is the Milliohm resistor. These resistors play a vital role in precision current sensing and power conversion, ensuring the seamless operation of modern telecommunication infrastructure. This article explores the potential of Milliohm resistors, their applications, and how they address specific challenges in the telecommunications industry.

Applications of Milliohm Resistors in Telecommunications
Milliohm resistors are integral to various applications within the telecommunications industry. They are used in power supplies, current sensing circuits, and voltage regulation systems. These applications benefit from the low resistance values of Milliohm resistors, which minimize power loss and ensure high efficiency.
| Application | Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supplies | Current Sensing | High Efficiency, Low Power Loss |
| Signal Processing | Signal Conditioning | Improved Signal Integrity |
| Power Conversion | DC-to-DC Conversion | Enhanced Power Management |
A Common Problem in Telecommunications
One of the most significant challenges in telecommunications infrastructure is the efficient management of power distribution. High current loads in telecommunication equipment can lead to significant power losses and overheating, which can degrade system performance and reliability. Traditional resistors often fail to provide the necessary precision and efficiency required for these applications.
Solution Using Milliohm Resistors
Milliohm resistors offer a solution to this problem by providing high precision and low resistance values. These resistors can handle high currents with minimal power loss, ensuring that telecommunication systems operate efficiently and reliably. By integrating Milliohm resistors into power distribution circuits, engineers can achieve better control over current flow, reduce heat generation, and enhance overall system performance.
Data and Analysis
The following table illustrates the performance differences between traditional resistors and Milliohm resistors in a typical telecommunication power supply application:
| Parameter | Traditional Resistor | Milliohm Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Value | 1 Ohm | 0.01 Ohm |
| Power Loss at 10A | 100W | 0.1W |
| Temperature Rise | High | Low |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
As shown in the table, Milliohm resistors significantly reduce power loss and temperature rise, leading to higher efficiency and improved system reliability.
Conclusion
Milliohm resistors are a game-changer in the telecommunications industry. By addressing the challenge of efficient power management, these resistors enhance the performance and reliability of telecommunication infrastructure. The integration of Milliohm resistors in power supplies, signal processing circuits, and power conversion systems ensures that modern telecommunication networks operate at peak efficiency. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of Milliohm resistors in unlocking the potential of telecommunication systems will only grow more critical.