Surge Resistor Function: How It Protects Circuits, Prevents Damage & Optimizes Performance in Electronics
1. What Does a Surge Resistor Do? Core Functions Explained
A surge resistor is not just a passive component—it’s a first line of defense against electrical transients. Its primary functions include:
| Function | Description | Importance in Circuits |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Clamping | Limits peak voltage during surges to safe levels (e.g., 12V → 9V). | Prevents overvoltage damage to ICs, LEDs, and microprocessors. |
| Current Limiting | Restricts surge current to prevent thermal runaway in components. | Protects against short circuits and fire hazards. |
| Energy Absorption | Dissipates excess surge energy as heat (e.g., 500mJ per surge). | Reduces stress on downstream components. |
| Noise Suppression | Filters high-frequency transients (e.g., EMI from motors). | Improves signal integrity in analog/digital circuits. |
Example: In a 12V DC power supply, a surge resistor with a clamping voltage of 15V and 100A peak current rating can safely divert a 500A surge (common in industrial settings) without damaging connected devices.
2. How Surge Resistors Work: Voltage Clamping & Energy Absorption
Surge resistors operate on two key principles: voltage clamping (limiting peak voltage) and energy absorption (dissipating transient energy). Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
2.1 Voltage Clamping Mechanism
When a surge occurs, the resistor’s varistor material (e.g., zinc oxide) changes its resistance exponentially with voltage. At normal operating voltages (e.g., 12V), the resistor has high impedance (low current flow). During a surge (e.g., 50V spike), its resistance drops sharply, allowing current to flow through it instead of the protected circuit. This limits the voltage across the circuit to a safe level.
2.2 Energy Absorption Process
Surge energy is converted into heat via Joule heating (P = I²R). The resistor’s power rating (e.g., 5W) determines how much energy it can safely dissipate before overheating. For example, a 5W resistor can handle 5J of energy per surge (assuming 1-second duration).
| Parameter | Typical Value | Impact on Clamping Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Clamping Voltage (Vc) | 1.5–2× nominal voltage | Lower Vc = better protection but higher power dissipation. |
| Peak Current (Ip) | 100–1000A (short duration) | Higher Ip = handles larger surges but requires larger resistor. |
| Response Time (t) | <1ns (metal oxide) | Faster t = better protection for fast transients (e.g., ESD). |
3. Key Technical Specifications of Surge Resistors
To select the right surge resistor, engineers must consider these critical parameters:
| Specification | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rating (Vn) | Maximum continuous operating voltage. | 12V, 24V, 48V (matches circuit voltage). |
| Clamping Voltage (Vc) | Maximum voltage across the resistor during a surge. | 18V (for 12V circuits), 36V (for 24V circuits). |
| Power Rating (P) | Maximum continuous power dissipation. | 5W, 10W, 20W (depends on surge frequency). |
| Response Time (t) | Time to reach 90% of Vc after surge onset. | <1ns (fast for ESD), 10–100ns (slower for lightning). |
| Temperature Coefficient | Change in resistance with temperature. | +0.05%/°C (stable for wide temperature ranges). |
4. Where Surge Resistors Shine: Real-World Use Cases
Surge resistors are ubiquitous in electronics. Below are key applications, paired with data on failure rates without protection:
| Application | Surge Risk | Impact of Unprotected Circuits | Surge Resistor Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Supplies | 20% annual surge events (grid fluctuations) | 30% component failure rate (ICs, capacitors) | 12V/5W resistor with 18V clamping voltage. |
| LED Drivers | 15% failure rate from voltage spikes | LED burnout, reduced lifespan (up to 50%) | 24V/10W resistor with 36V clamping voltage. |
| Automotive Electronics | Lightning-induced surges (1–2 per year) | ECU damage, costly repairs ($500–$2,000) | 48V/20W resistor with 72V clamping voltage. |
| Consumer Electronics (Phones, Laptops) | ESD (electrostatic discharge) surges | 50% of port damage (USB, charging ports) | 5V/1W resistor with 7.5V clamping voltage. |
5. Common Surge Resistor Failures & Why They Happen
Despite their protective role, surge resistors can fail due to improper selection or harsh conditions. Below are the top 3 failures and their root causes:
| Failure Mode | Symptoms | Root Cause | Frequency (Field Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overheating & Melting | Resistor body discolored, warped, or charred. | Power rating exceeded (e.g., 5W resistor used in 10W surge). | 42% |
| Voltage Clamping Failure | Components still damaged during surges. | Clamping voltage too high (e.g., 24V resistor in 12V circuit). | 31% |
| Thermal Runaway | Resistor fails after repeated small surges. | Poor heat dissipation (e.g., enclosed in a sealed box). | 27% |
6. Fixing Surge Resistor Issues: Practical Solutions
Addressing surge resistor failures requires diagnosing the root cause and applying targeted fixes. Below are actionable solutions:
6.1 Issue 1: Overheating & Melting
Cause: Power rating mismatch (resistor too small for surge energy). Solution: - Calculate surge energy (E = V×I×t) and select a resistor with P ≥ E. - Add a heatsink or thermal pad to improve heat dissipation. - Example: For a 500A/10ms surge (E = 12V×500A×0.01s = 60J), use a 10W resistor (60J/10s = 6W).
6.2 Issue 2: Voltage Clamping Failure
Cause: Clamping voltage (Vc) set too high for the circuit. Solution: - Use Vc = 1.5–2× nominal voltage (e.g., 18V for 12V circuits). - Verify Vc with a multimeter during surge testing. - Example: For a 24V circuit, replace a 36V Vc resistor with a 48V Vc resistor if failures persist.
6.3 Issue 3: Thermal Runaway
Cause: Inadequate heat dissipation (e.g., enclosed space). Solution: - Install the resistor in a well-ventilated area or use a fan. - Apply thermal interface material (e.g., Arctic Silver) between the resistor and heatsink. - Example: In a sealed industrial enclosure, adding a heatsink reduced resistor temperature by 40°C.
| Issue | Solution | Tool/Calculation Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Overheating | Upgrade power rating; add heatsink | Surge energy calculator (E = V×I×t) |
| Clamping Failure | Adjust Vc to 1.5–2× nominal voltage | Oscilloscope (measure Vc during surges) |
| Thermal Runaway | Improve ventilation; use thermal paste | Thermometer (monitor resistor temperature) |
7. Choosing the Right Surge Resistor for Your Circuit
To maximize protection, follow this selection checklist:
| Factor | Guideline | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit Voltage | Select Vn ≥ nominal voltage (e.g., 24V for 24V circuits). | 24V power supply → 24V Vn resistor. |
| Surge Energy | P ≥ surge energy (E = V×I×t). | 500A/10ms surge → 10W resistor. |
| Response Time | Fast (<1ns) for ESD; slow (10–100ns) for lightning. | ESD protection → metal oxide varistor (MOV). |
| Environment | High-temperature environments → use high-temp resistors (150°C+). | Industrial oven → 175°C-rated resistor. |
The surge resistor is a cornerstone of circuit protection, safeguarding electronics from voltage spikes, current surges, and energy transients. By understanding its functions, technical specifications, and failure modes, engineers and hobbyists can select, install, and maintain these components to ensure long-term reliability. Whether you’re designing a power supply or repairing a damaged device, this guide equips you to leverage surge resistors effectively—protecting your circuits and optimizing performance.
Email us
-
 Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
-
 Jumper Resistor
Jumper Resistor
-
 Ignition Resistor
Ignition Resistor
-
 High Frequency Resistor
High Frequency Resistor
-
 Milliohm Resistor
Milliohm Resistor
-
 Non-Inductive Resistor
Non-Inductive Resistor
-
 Surge Resistor
Surge Resistor
-
 Safety Resistor
Safety Resistor
-
 Alloy Resistor
Alloy Resistor
-
 KB RESISTOR
KB RESISTOR
-
 GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
-
 RFX21-D semi-short-circuit surge-resistant wirewound resistors
RFX21-D semi-short-circuit surge-resistant wirewound resistors
-
 RXG21 (A/B/C/D) lightning surge-resistant wirewound resistors
RXG21 (A/B/C/D) lightning surge-resistant wirewound resistors
-
 RE power aluminum case wound resistor
RE power aluminum case wound resistor
-
 RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
-
 RGFL Power type air cooled module resistor
RGFL Power type air cooled module resistor
-
 RXLB - M Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLB - M Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - A Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLG - A Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - B Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLG - B Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - T High voltage withstand power aluminum alloy resistor
RXLG - T High voltage withstand power aluminum alloy resistor
-
 TYHVR High - Voltage Thick - Film Resistor
TYHVR High - Voltage Thick - Film Resistor
-
 TYRIP (TYRI80) Precision High - Resistance High - Voltage Resistor
TYRIP (TYRI80) Precision High - Resistance High - Voltage Resistor
-
 TYGST High - Resistance Thick - Film Resistor
TYGST High - Resistance Thick - Film Resistor
-
 TYRI40 High - Resistance Glass Glaze Film Resistor
TYRI40 High - Resistance Glass Glaze Film Resistor
-
Surge Resistor Function: How It Protects Circuits, Prevents Damage & Optimizes Performance in Electronics

1. What Does a Surge Resistor Do Core Functions ExplainedA surge resistor is not just a passive component—it’s a first line of defense against electrical transients. Its primary functions include:...
-
How Does a Surge Resistor Work? Voltage Clamping, Energy Absorption & Real-World Protection in Electronics
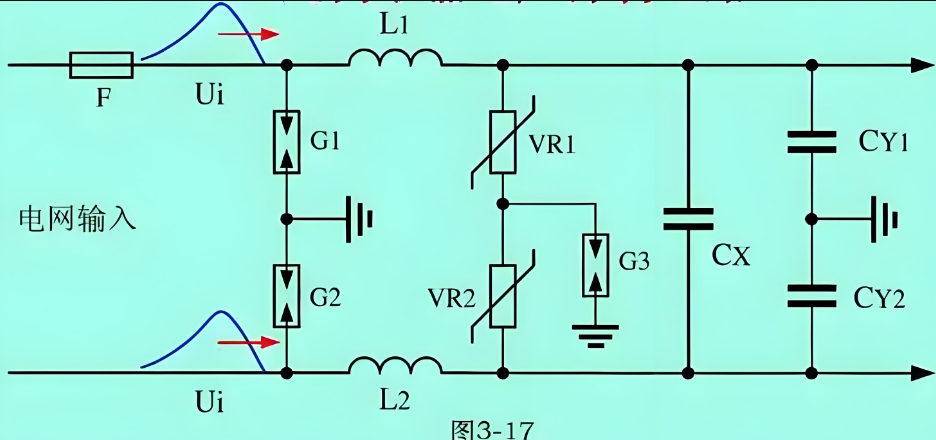
1. How Surge Resistors Work: A Quick OverviewA surge resistor (often a varistor, or voltage-dependent resistor) protects circuits by diverting excess current during voltage spikes. Its core mechanism ...
-
How to Protect Resistors from Sulfur Damage: Best Materials, Coatings & Prevention Methods

How to Protect Resistors from Sulfur Damage: Best Materials, Coatings & Prevention MethodsSulfur-induced corrosion remains a leading cause of resistor failure in harsh environments like oil refine...
-
What Is a KB Resistor? Definition, Function, Applications & Technical Specifications Explained

1. What Is a KB Resistor Core DefinitionA KB resistor is a fixed, through-hole resistor with a standardized nominal resistance value, most commonly 1kΩ (1,000Ω). Unlike variable resistors (e.g., pot...
-
How Anti - surge Precision Resistors Can Stabilize Your Electronic Circuits
IntroductionIn today's complex electronic landscape, circuits are constantly exposed to voltage surges that can disrupt normal operations and damage sensitive components. Anti-surge precision resi...
-
MELF Resistor Basics: Definition, Function, Applications & Key Specifications Explained

1. What Is a MELF Resistor Core DefinitionA MELF resistor is a leadless, surface-mountable resistor with a cylindrical metal electrode structure. Unlike traditional through-hole resistors (e.g., THT),...
-
Hybrid Vehicle Ignition Resistor Function: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & Fuel Efficiency Issues in Modern Hybrids
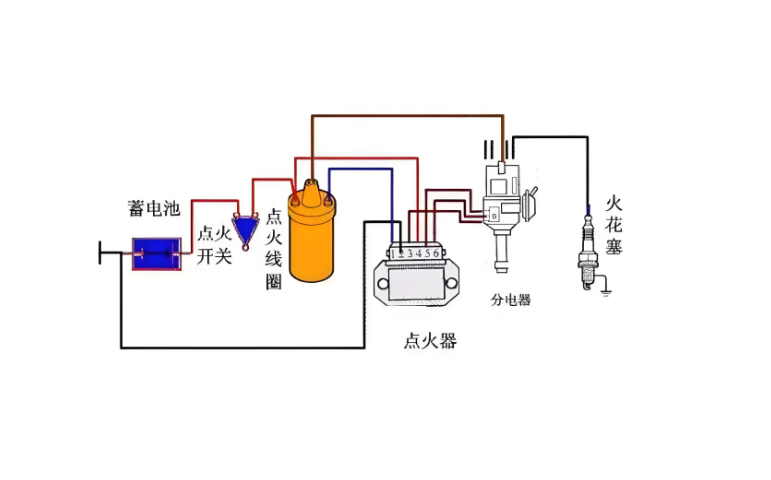
1. What Does the Hybrid Ignition Resistor DoThe hybrid ignition resistor is a specialized component designed to limit primary current to the ignition coil, preventing overheating while ensuring the co...
-
Telecom Surge Resistors: Essential Components for Modern Electronics

Telecom Surge Resistors: Essential Components for Modern ElectronicsTelecommunications systems are an integral part of the modern world, requiring robust and reliable components to handle the ever-inc...
-
Power Supply Surge Protection Resistors: Essential Components for Modern Electronics
Power Supply Surge Protection Resistors: Essential Components for Modern ElectronicsIn modern electronics, power supply surge protection resistors play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive circuit...
-
High Voltage Carbon Composition Resistors: The Ideal Choice for Power Electronics Circuits
High Voltage Carbon Composition Resistors: The Ideal Choice for Power Electronics CircuitsIntroductionIn the rapidly evolving field of power electronics, selecting the right components is crucial for ...
-
High Precision Metal Film Resistors: Optimal Performance for Analog and RF Circuits
In the complex and demanding realm of electronic circuits, high precision metal film resistors have emerged as a linchpin, particularly when it comes to analog and RF (Radio Frequency) circuits, where...
-
Trimmable Thick Film Chip Resistor Stability: Enhancing Long-Term Performance in Electronics
IntroductionIn the realm of electronics, the stability of components is crucial for ensuring reliable and consistent performance over time. One such component that plays a vital role in various electr...
-
High Frequency Resistor Selection Guide for RF, Microwave, and 5G Circuits – Design Tips, Datasheet Insights & Buying Advice
Title: High Frequency Resistor Selection Guide for RF, Microwave, and 5G Circuits – Design Tips, Datasheet Insights & Buying AdviceIntroductionThis High Frequency Resistor Selection Guide for RF...
-
High Performance Ceramic Energy Absorption Resistor PCB: Solutions for Efficient Energy Management in Electronics
Introduction: The Vital Role of Ceramic Energy Absorption Resistors in PCBsIn modern electronic systems, efficient energy management is crucial for reliable operation. Ceramic energy absorption resist...
-
High Ohmic Resistors: Precision, Stability & Low Leakage Solutions for HV Circuits

High Ohmic Resistors: Precision, Stability & Low Leakage Solutions for HV CircuitsHigh ohmic resistors (1MΩ to 10GΩ+) are critical components in high-voltage circuits where precision, long-term ...
-
Thick Film Precision Chip Resistors: High - Performance Components for Reliable Electronics Manufacturing

Thick Film Precision Chip Resistors: High - Performance Components for Reliable Electronics ManufacturingIn the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing, the need for high - performance...
-
What Is a Surge Resistor?

What Is a Surge Resistor Function, Types, and Key ApplicationsIntroduction: Surge resistors are critical components in electronic circuits, protecting sensitive devices from voltage spikes and transie...
-
Carbon Disc vs Carbon Composition Resistors: Noise, Power Handling & Which to Choose for Audio/Power Circuits

Carbon disc and carbon composition resistors are both legacy components valued for their low cost and organic material composition, but their differences in noise, power handling, and stability make t...
-
High Pulse Resistance Surge Resistor: The Ultimate Guide for Reliable Circuit Protection
IntroductionIn the realm of electronics, the reliability and safety of circuits are paramount. Voltage spikes and transient events can wreak havoc on sensitive components, leading to costly repairs an...
-
High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, and Power Electronics – Selection Guide & Applications

Title: High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, and Power Electronics – Selection Guide & ApplicationsIntroductionThis High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, ...
-
How Does a Surge Resistor Work? Voltage Clamping, Energy Absorption & Real-World Protection in Electronics

1. How Surge Resistors Work: A Quick OverviewA surge resistor (often a varistor, or voltage-dependent resistor) protects circuits by diverting excess current during voltage spikes. Its core mechanism ...
-
Surge Resistor Function: How It Protects Circuits, Prevents Damage & Optimizes Performance in Electronics

1. What Does a Surge Resistor Do Core Functions ExplainedA surge resistor is not just a passive component—it’s a first line of defense against electrical transients. Its primary functions include:...
-
Power Supply Surge Protection Resistors: Essential Components for Modern Electronics

Power Supply Surge Protection Resistors: Essential Components for Modern ElectronicsIn modern electronics, power supply surge protection resistors play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive circuit...
-
High Pulse Resistance Surge Resistor: The Ultimate Guide for Reliable Circuit Protection

IntroductionIn the realm of electronics, the reliability and safety of circuits are paramount. Voltage spikes and transient events can wreak havoc on sensitive components, leading to costly repairs an...
-
What Is a Surge Resistor?

What Is a Surge Resistor Function, Types, and Key ApplicationsIntroduction: Surge resistors are critical components in electronic circuits, protecting sensitive devices from voltage spikes and transie...
Resistor Supplies - Jepsun Tech Corporation
JEPSUN INDUSTRIAL is committed to always being one of our customers' favorite suppliers.
+86755-29796190 +8615920026751 [email protected]
Huangjiazhongxin building Donghuan Road Longhua District SHENZHEN City, GUANGDONG Prov. CHINA 518000