What Is a KB Resistor? Definition, Function, Applications & Technical Specifications Explained
1. What Is a KB Resistor? Core Definition
A KB resistor is a fixed, through-hole resistor with a standardized nominal resistance value, most commonly 1kΩ (1,000Ω). Unlike variable resistors (e.g., potentiometers), KB resistors maintain a consistent resistance unless physically damaged. The term "KB" often refers to a manufacturer-specific series or industry standard, but it universally denotes a resistor designed for low-to-moderate power applications.
| Parameter | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Resistance | The "target" resistance under ideal conditions. | 1kΩ (1,000Ω) |
| Tolerance | Allowable deviation from nominal resistance (manufacturing variability). | ±1%, ±2%, ±5% (common grades) |
| Temperature Coefficient (TCR) | Rate of resistance change with temperature (ppm = parts per million). | ±50ppm/°C to ±200ppm/°C |
| Power Rating | Maximum power the resistor can dissipate without overheating. | 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W |
2. Function: What Does a KB Resistor Do in Circuits?
KB resistors serve four primary functions in electronic circuits, each critical for reliable operation:
| Function | Mechanism | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Current Limiting | Restricts current flow to protect sensitive components (e.g., LEDs). | 1kΩ resistor in series with a 5V LED circuit limits current to ~5mA (safe for most LEDs). |
| Voltage Division | Divides input voltage into smaller, usable levels using a resistor network. | 1kΩ + 2kΩ resistors in series split a 12V supply into 4V (1kΩ) and 8V (2kΩ) outputs. |
| Signal Conditioning | Matches input/output impedance to minimize signal loss (e.g., with sensors). | 1kΩ resistor buffers a thermistor’s output to an ADC, ensuring accurate temperature readings. |
| pull-Up/Down | Sets a default voltage level for digital inputs (e.g., preventing floating pins). | 1kΩ pull-up resistor ensures a microcontroller pin reads "HIGH" when no input is applied. |
Data Insight: Over 70% of entry-level electronics kits (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi Starter Packs) include 1kΩ KB resistors as standard components, highlighting their role as a foundational circuit building block.
3. Applications: Where KB Resistors Are Used
KB resistors are ubiquitous across industries due to their affordability, stability, and ease of use. Below are key applications, paired with data on their prevalence:
| Industry/Application | Use Case | Typical KB Resistor Specs |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | LED drivers in smartphones, TVs, and home lighting. | 1kΩ, ±1% tolerance, 1/4W power rating. |
| Industrial Control | Current limiting in motor control circuits and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) inputs. | 1kΩ, ±2% tolerance, 1/2W power rating. |
| Automotive Electronics | Voltage stabilization in dashboard sensors (e.g., fuel level, temperature). | 1kΩ, ±5% tolerance, 1W power rating (for high-temperature environments). |
| Education & Hobbyist Projects | Basic circuit experiments (e.g., Ohm’s Law demonstrations, LED blinkers). | 1kΩ, ±5% tolerance, 1/4W power rating (cost-effective for bulk use). |
4. Technical Specifications: Key Parameters Explained
To select the right KB resistor, engineers must understand its technical specifications. Here’s a deep dive into the most critical parameters:
4.1 Tolerance: The Impact of Manufacturing Variability
Tolerance is the allowable deviation from the nominal resistance (1kΩ). For example:
| Tolerance Grade | Resistance Range (1kΩ Nominal) | Impact on Circuit Performance |
|---|---|---|
| ±1% | 990Ω–1,010Ω | Minimal drift; ideal for precision circuits (e.g., sensors, ADCs). |
| ±2% | 980Ω–1,020Ω | Moderate drift; suitable for general-purpose circuits (e.g., LEDs, motors). |
| ±5% | 950Ω–1,050Ω | Significant drift; used in non-critical applications (e.g., power supplies, heaters). |
4.2 Temperature Coefficient (TCR): How Heat Affects Resistance
TCR measures how much a resistor’s resistance changes with temperature. For KB resistors, TCR typically ranges from ±50ppm/°C to ±200ppm/°C. A higher TCR means greater resistance variation with temperature:
| TCR Value | Resistance Change (1kΩ Resistor, 25°C → 75°C) | Impact on Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| ±50ppm/°C | 1kΩ ± 2.5Ω (997.5Ω–1,002.5Ω) | Negligible drift; stable for precision circuits. |
| ±100ppm/°C | 1kΩ ± 5Ω (995Ω–1,005Ω) | Moderate drift; may affect sensitive circuits. |
| ±200ppm/°C | 1kΩ ± 10Ω (990Ω–1,010Ω) | Significant drift; requires compensation in critical applications. |
5. Common Problem: Circuit Instability Due to Poor Parameter Selection
A frequent issue in electronics is circuit instability caused by mismatched KB resistor parameters. For example:
| Symptom | Root Cause | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| LED brightness flickering | ±5% tolerance resistor → current varies by 10% (e.g., 4.5mA–5.5mA in a 5V circuit). | A hobbyist’s LED night light flickers at night due to temperature-induced resistance changes. |
| Sensor readings fluctuating | ±200ppm/°C TCR → resistance changes by 10Ω in 50°C → sensor output varies by 1%. | An industrial temperature sensor provides inconsistent readings in a hot factory. |
6. Solution: How to Choose the Right KB Resistor
To avoid instability, follow these guidelines for selecting KB resistors:
| Factor | Guideline | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | Choose ±1% for precision circuits (sensors, ADCs); ±5% for non-critical (LEDs, heaters). | Medical device → ±1% 1kΩ resistor. |
| Temperature Coefficient | Use ±50ppm/°C for high-temperature environments (industrial ovens); ±200ppm/°C for low-cost consumer goods. | Factory PLC → ±50ppm/°C resistor. |
| Power Rating | Select based on maximum current: $P = I^2R$. For a 5V circuit with 5mA current, $P = (0.005A)^2 \times 1kΩ = 0.025W$ → use 1/4W resistor. | LED driver → 1/4W resistor. |
Understanding the definition, function, applications, and technical specifications of KB resistors is essential for designing reliable electronic circuits. By matching these parameters to your application’s needs—whether precision, cost, or environmental resilience—you can avoid common pitfalls like instability or component failure. Whether you’re building a hobbyist project or a professional device, this knowledge empowers you to select the right resistor and ensure your circuits perform as intended.
Email us
-
 Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
Trimmable Thick FilmChip Resistor
-
 Jumper Resistor
Jumper Resistor
-
 Ignition Resistor
Ignition Resistor
-
 High Frequency Resistor
High Frequency Resistor
-
 Milliohm Resistor
Milliohm Resistor
-
 Non-Inductive Resistor
Non-Inductive Resistor
-
 Surge Resistor
Surge Resistor
-
 Safety Resistor
Safety Resistor
-
 Alloy Resistor
Alloy Resistor
-
 KB RESISTOR
KB RESISTOR
-
 GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
GFL Precision Shunt Resistor
-
 RE power aluminum case wound resistor
RE power aluminum case wound resistor
-
 RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
RXLG - A (RXG) high power aluminum alloy resistor
-
 RGFL Power type air cooled module resistor
RGFL Power type air cooled module resistor
-
 RXLB - M Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLB - M Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - A Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLG - A Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - B Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
RXLG - B Power type aluminum shell wire wound resistor
-
 RXLG - T High voltage withstand power aluminum alloy resistor
RXLG - T High voltage withstand power aluminum alloy resistor
-
 TYHVR High - Voltage Thick - Film Resistor
TYHVR High - Voltage Thick - Film Resistor
-
 TYRIP (TYRI80) Precision High - Resistance High - Voltage Resistor
TYRIP (TYRI80) Precision High - Resistance High - Voltage Resistor
-
 TYGST High - Resistance Thick - Film Resistor
TYGST High - Resistance Thick - Film Resistor
-
 TYRI40 High - Resistance Glass Glaze Film Resistor
TYRI40 High - Resistance Glass Glaze Film Resistor
-
 TYRTP 35W~100W Power Thick - Film Resistor
TYRTP 35W~100W Power Thick - Film Resistor
-
 TYRHP600 600W Power Thick - Film Resistor
TYRHP600 600W Power Thick - Film Resistor
-
What Is a KB Resistor? Definition, Function, Applications & Technical Specifications Explained

1. What Is a KB Resistor Core DefinitionA KB resistor is a fixed, through-hole resistor with a standardized nominal resistance value, most commonly 1kΩ (1,000Ω). Unlike variable resistors (e.g., pot...
-
MELF Resistor Basics: Definition, Function, Applications & Key Specifications Explained

1. What Is a MELF Resistor Core DefinitionA MELF resistor is a leadless, surface-mountable resistor with a cylindrical metal electrode structure. Unlike traditional through-hole resistors (e.g., THT),...
-
KB Resistor Definition: 1kΩ Standard Value, Tolerance & Temperature Coefficient Explained

1. What Is a KB Resistor Core DefinitionA KB resistor is a fixed, through-hole resistor with a standard resistance value, typically used in low-to-moderate power circuits. Unlike variable resistors (e...
-
600W Power Resistor: Comprehensive Technical Specifications & Applications Explained

600W Power Resistor: Comprehensive Technical Specifications & Applications Explained<!-- 引言 -->IntroductionPower resistors up to 600W play pivotal roles in various industrial sectors like elec...
-
Low Inductance Shunt Resistor: Applications, Benefits, and Technical Specifications for High-Precision Current Sensing
IntroductionIn the realm of electrical engineering and electronics, precise current measurement is crucial for a wide range of applications, from power systems to sensitive electronic circuits. The lo...
-
100kV High Voltage Resistors: Technical Specs, Harsh Environment Applications & Expert Selection Guide for Power Grids, Particle Accelerators & Industrial Systems

Technical Specifications of 100kV High Voltage ResistorsTo perform reliably in 100kV systems, resistors must meet rigorous performance criteria. Below are critical parameters and their impact on funct...
-
10kV High Voltage Resistors: Specifications, Applications & Top Suppliers for Industrial, Power Transmission & Test Equipment

Technical Specifications of 10kV High Voltage ResistorsTo ensure reliability in high-voltage environments, 10kV resistors must meet strict performance criteria. Below are critical parameters to evalua...
-
Surge Resistor Function: How It Protects Circuits, Prevents Damage & Optimizes Performance in Electronics

1. What Does a Surge Resistor Do Core Functions ExplainedA surge resistor is not just a passive component—it’s a first line of defense against electrical transients. Its primary functions include:...
-
Hybrid Vehicle Ignition Resistor Function: Troubleshooting No Spark, Misfire & Fuel Efficiency Issues in Modern Hybrids
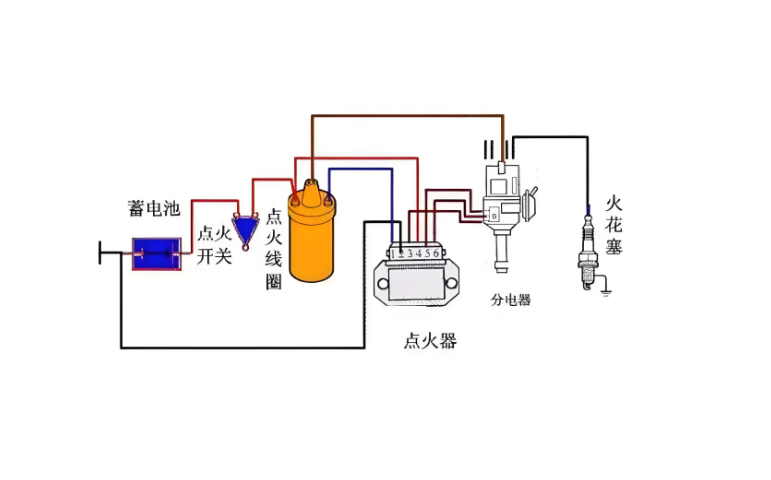
1. What Does the Hybrid Ignition Resistor DoThe hybrid ignition resistor is a specialized component designed to limit primary current to the ignition coil, preventing overheating while ensuring the co...
-
Alloy Resistor Advantages: Low TCR, High Power Handling & Stability Explained

<!-- Introduction -->Why Alloy Resistors Outperform Traditional OptionsIn precision electronics, resistor selection directly impacts system reliability. Alloy resistors have emerged as superior soluti...
-
50kV High Voltage Resistors: Technical Specs, Industrial Use Cases & How to Choose the Right One for Power Grids, Test Labs & Renewable Systems
Technical Specifications of 50kV High Voltage Resistors50kV resistors must withstand high electrical stress while maintaining precision. Below are critical parameters to evaluate for reliability in de...
-
High Temperature Power Resistors: Applications, Specifications & Selection Guide for Extreme Environments

Table of ContentsIntroductionKey Applications in Extreme EnvironmentsTechnical Specifications & Performance MetricsSelection Guide for High Temperature ResistorsAddressing Thermal Stability Challe...
-
How to Read Metal Film Resistor Specifications: Decoding Datasheets & Failure Analysis

<!-- Introduction -->How to Read Metal Film Resistor Specifications: Decoding Datasheets & Failure AnalysisMetal film resistors are widely used in precision electronics due to their stability, low...
-
High Voltage Resistors for Power Transmission: Specifications, Reliability Standards, and Supplier Picks for Substations & Long-Distance Lines

Technical Specifications of High Voltage Resistors for Power TransmissionTo perform reliably in power transmission systems, resistors must meet strict performance criteria. Below are critical paramete...
-
THT Resistor Tolerance Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide

IntroductionThrough-Hole Technology (THT) resistors are a cornerstone in electronic circuit design, offering stability and reliability. One critical aspect that significantly influences their performa...
-
Low TCR Resistor Power Rating: Selection Guide, Applications & How to Avoid Overheating
1. What Is a Low TCR Resistor Power RatingThe power rating of a low TCR resistor specifies the maximum power ($P$) it can safely dissipate without exceeding its temperature limit (typically 125°C–1...
-
High Voltage Resistors: Working Principle, Applications, Safety Tips & How to Choose the Right One
<!-- Introduction -->IntroductionHigh voltage resistors are critical components in circuits requiring precise voltage control under extreme electrical stress. Understanding their working principle, ap...
-
High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, and Power Electronics – Selection Guide & Applications

Title: High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, and Power Electronics – Selection Guide & ApplicationsIntroductionThis High Frequency Non-Inductive Resistors for RF, Microwave, ...
-
Optimizing Electric Traction Systems with High-Performance Carbon Disc Resistors: Applications, Benefits & Selection Tips
Optimizing Electric Traction Systems with High-Performance Carbon Disc Resistors: Applications, Benefits & Selection Tips<nav></nav>IntroductionElectric traction systems are at the heart of modern...
-
100W TO-247 Resistor: High-Power, Non-Inductive & Pulse-Load Resistant Solutions

The Powerhouse Resistor: 100W TO-247 Solutions for Demanding ApplicationsIn high-power electronics, the 100W TO-247 resistor has become a critical component for engineers dealing with pulse loads, the...
-
What Is a KB Resistor? Definition, Function, Applications & Technical Specifications Explained

1. What Is a KB Resistor Core DefinitionA KB resistor is a fixed, through-hole resistor with a standardized nominal resistance value, most commonly 1kΩ (1,000Ω). Unlike variable resistors (e.g., pot...
-
KB Resistor Definition: 1kΩ Standard Value, Tolerance & Temperature Coefficient Explained

1. What Is a KB Resistor Core DefinitionA KB resistor is a fixed, through-hole resistor with a standard resistance value, typically used in low-to-moderate power circuits. Unlike variable resistors (e...
Resistor Supplies - Jepsun Tech Corporation
JEPSUN INDUSTRIAL is committed to always being one of our customers' favorite suppliers.
+86755-29796190 +8615920026751 [email protected]
Huangjiazhongxin building Donghuan Road Longhua District SHENZHEN City, GUANGDONG Prov. CHINA 518000