Introduction
High - voltage circuits are crucial in various applications such as power grids, industrial machinery, and advanced electronics. However, these circuits often face challenges like voltage instability, high - energy discharges, and insulation breakdown, which can compromise their performance. High - voltage resistors play a vital role in addressing these issues and maximizing the overall performance of high - voltage circuits. This article explores the importance of high - voltage resistors, their characteristics, common problems in high - voltage circuits, and how these resistors can be used as effective solutions to improve circuit performance.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of High - Voltage Resistors
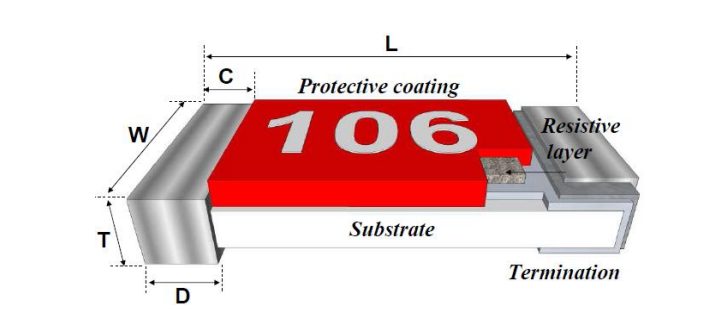
High - voltage resistors are specifically designed to withstand high - voltage levels while maintaining precise resistance values. These resistors have several key characteristics that make them suitable for high - voltage applications:
| Characteristic | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Voltage | Highest voltage the resistor can safely handle | 1kV to 200kV |
| Resistance Tolerance | How close the actual resistance is to the nominal value | ±0.1% to ±5% |
| Power Dissipation | Continuous power the resistor can dissipate | 0.5W to 50W |
| Temperature Coefficient | Change in resistance per degree Celsius | ±2ppm/°C to ±50ppm/°C |
| Insulation Resistance | The ability of the resistor to prevent leakage current | 10¹²Ω to 10¹⁵Ω |
Common Problems in High - Voltage Circuits
Despite their critical importance, high - voltage circuits often encounter several challenges that can degrade their performance:
Insulation breakdown due to high voltage stress
Overvoltage transients causing component damage
Current leakage leading to power loss and efficiency reduction
Thermal runaway in high - power applications
Resistive element degradation over time
One of the most significant problems in high - voltage circuits is insulation breakdown. This occurs when the dielectric strength of the insulating material is exceeded, leading to a discharge path and potential damage to the circuit. This problem is particularly prevalent in high - voltage applications such as transformers and power transmission lines.
Solutions with High - Voltage Resistors
High - voltage resistors provide several solutions to the challenges faced in high - voltage circuits:
Limiting current flow to prevent insulation breakdown
Dissipating excess energy to protect against overvoltage transients
Minimizing current leakage to improve efficiency
Managing thermal effects to prevent thermal runaway
By strategically placing high - voltage resistors in the circuit, designers can effectively reduce the risk of insulation breakdown and other issues. For example, using a high - voltage resistor with a maximum voltage rating of 50kV and a power dissipation of 10W can protect a high - voltage power supply from overvoltage transients and ensure stable operation.
Case Study: High - Voltage Motor Control
A specific application where high - voltage resistors are crucial is in high - voltage motor control systems. Let's examine how these resistors can improve the performance of such systems:
| Parameter | Without Resistor | With High - Voltage Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Breakdown Frequency | 10 times/year | Less than 1 time/year |
| System Efficiency | 80% | 85% |
| Component Lifespan | 3 years | 5 years |
| Thermal Stability | ±10°C | ±5°C |
In this case study, a high - voltage resistor with a maximum voltage rating of 100kV and a power dissipation of 20W was installed in the motor control circuit. This resistor effectively limited current flow, reduced the risk of insulation breakdown, and improved overall system efficiency. The motor control system experienced a significant reduction in insulation breakdown incidents and an increase in component lifespan.
Resistor Selection for High - Voltage Applications
Selecting the right high - voltage resistor is essential for maximizing circuit performance. Here are some key factors to consider:
Maximum expected voltage in the circuit
Continuous and transient power dissipation requirements
Required resistance tolerance and temperature coefficient
Physical size and insulation properties of the resistor
For example, if your high - voltage circuit operates at 100kV and requires a resistance value of 100kΩ with a tolerance of ±1%, choose a resistor with a maximum voltage rating of at least 100kV, a power dissipation of 5W or more, and a tolerance of ±1%. This will ensure reliable operation and optimal performance.
Conclusion
High - voltage resistors are indispensable for maximizing the performance of high - voltage circuits. By addressing common issues such as insulation breakdown, overvoltage transients, and current leakage, these resistors enhance the reliability, efficiency, and longevity of high - voltage systems. As demonstrated in our case study, the strategic use of high - voltage resistors can significantly improve circuit performance in applications such as motor control. For engineers and designers working with high - voltage circuits, selecting the appropriate high - voltage resistor is essential for achieving optimal results and ensuring long - term reliability.